The Tax Code of the Russian Federation allows taking into account the costs incurred by the company to pay for marketing services when calculating income tax (subclause 27, clause 1, article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). But due to the fact that the costs of marketing agreements are sometimes used to optimize tax payments, tax authorities often question the reality of such transactions. And companies themselves make many mistakes when documenting such expenses.
To avoid fiscal risks, you need to competently draw up accompanying documentation. In addition, such a document as the regulation on marketing policy, will help defend the right to take into account disputed expenses. Therefore, you should not leave its preparation to the marketing department. It is necessary to pay attention to other documents accompanying transactions for the provision of marketing services.
Regulations on the company's marketing policy
There is no unified form of the regulation. When preparing this document, it is important to take into account the specific features of your company. Therefore, it would be a mistake to blindly copy the marketing policy of another organization; it is not a fact that it will be universal. Despite the fact that the document is drawn up primarily for internal use, it is important that it is properly formatted. Correctly and completely indicate the company details and the date of preparation of the document.
Marketing policies may require periodic promotions to increase sales. Growing companies need to spend on market research. And such a complex system as a loyalty program or the procedure for providing discounts and bonuses needs to be described in as much detail as possible. The Russian Ministry of Finance allows the corresponding expenses to be accepted as a reduction in tax profit only if they are aimed at further increasing income or expanding client base(letter dated August 4, 2009 No. 03-03-06/1/513). The regulation may consist, for example, of the following sections: “Sales policy”, “Pricing”, “Loyalty program”, “ Information services", "Advertising", etc.
Of course, marketers and advertisers will take on most of the work, but it is in your interests to ensure that each type of marketing and consulting expense has its own compelling purpose and economic justification. The application should include forms of accompanying documents and reports. The head of the company can approve the position by issuing an order. A sample of such an order is given below.
Please note: if the company is small and marketing costs are also insignificant, it is not necessary to issue a separate regulation. You can simply add a new section to accounting policy, where information on the accounting procedure for relevant costs will be disclosed.
Other documents confirming marketing expenses
Of course, to confirm the expenses incurred by the company, a marketing policy statement alone will not be enough. It is important to stock up on a comprehensive package of documents. Such documents include the following papers.
Agreement and acceptance certificate for services provided. As with any other transaction, the procedure for providing marketing services is specified in the contract. In it, the parties reflect terms, prices and other important conditions. And the form of the act must contain all the required details.
Analytical information. In practice, few companies prepare such a certificate. Although it can become one of the main arguments when communicating with tax authorities. In it, a company that is about to enter into an agreement for the provision of marketing services explains why the decision was made to launch a particular project. In addition, the certificate can indicate exactly what results the company expects from this cooperation (providing information about the sales or sales market, competitors or consumer demand, calculating the effectiveness of the project and the procedure for its implementation, etc.). At the end, you need to describe how the marketing services received can positively influence the fate of the company. This will serve economic justification, which is required by Article 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The certificate will be useful if marketing services are provided by a third-party organization, although the company has specialists of the same profile. This situation always worries inspectors: why spend extra money on someone else’s specialists when the company has employees with the same position and specialization? Your response should consist of the following documents:
- an agreement for the provision of marketing services, which clearly defines the functions of third-party specialists;
- job description of full-time employees with a comprehensive list of their work tasks;
- analytical report with a list of reasons why third-party specialists are involved for certain events. Such reasons include the lack of necessary qualifications and skills among full-time employees, a shortage of specialists due to the large volume of work, or the lack of job description those tasks that need to be performed in a particular case.
Please note: in documents for the provision of marketing services, it is better to use the term “current market research”. It is these expenses that can be taken into account in accordance with subparagraph 27 of paragraph 1 of Article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Written report. It is important not only to draw up an acceptance certificate for the services provided, but also to ensure that the counterparty formalizes all the requested information in writing. For example, this could be a written consultation, the results of an ongoing market research with practical recommendations etc.
In practice, tax authorities check such reports especially carefully. According to tax officials, reports must contain the information required by Article 33 of the International Marketing Research Code of 1976. For example, “a description of the expected and actual scope of the problems”, “details of the method of studying the subject of research, as well as the weighing (evaluation) methods used”, etc. In addition to the final document, sometimes controllers also request monthly reports from the contractor on the work done.
An order from the manager to apply the information obtained through research. This document will once again confirm that the information is useful and will be used in the course of business activities.
An order will be needed if, for example, the costs of market research did not entail an expansion of production and an increase in sales volumes. In such a situation, tax authorities may consider these costs not economically justified, since they did not lead to an increase in profits. However, the rule “a negative result is also a result” applies here. The justification of the costs can be confirmed by a report on the work done by the contractor. It should contain analytical information, data about competitors in this market, forecasts for a decrease in income if the company enters new market or production of a new product.
Thus, if the company had not spent funds on marketing research, it would suffer a loss from entering a new market, since in this territory, for example, there is low demand, oversaturation of goods or high competition. Therefore, by spending on research, the company saved itself from major financial losses, which is confirmed by economic feasibility cooperation.
Alexander Elin,
Director of the company "ACADEMY OF AUDIT"
Competitive advantage is that unique difference
implement within 6 months.
Reliable Development Team
Marketing Management References
How many spend for marketing and advertising
What questions will you find answers to in this article?
- What costs should be classified as marketing?
- Which method to choose to determine marketing budget
- What numbers to focus on when approving marketing budget
- How to calculate marketing budget
Correctly calculated marketing budget will allow the company not to lose its market share and without incurring additional costs. Definition task marketing budget is relevant for all companies that have a marketing department or other service that performs marketing functions (more details about the tasks solved by marketing departments.
What is included in marketing costs?
Marketing costs are all the company's expenses necessary to implement marketing activities. They can be divided into three types:
- Organizational costs (creation and maintenance of a marketing department).
- Costs of strategic marketing (strategy development).
- Tactical marketing costs.
Although the costs of organizing and developing a strategy are much less than advertising (included in tactical marketing), the costs of the first two types are extremely important, and the problems associated with them must be considered separately. The solutions proposed in this article will only concern the costs of tactical marketing(*).
IN general view budget investments in tactical marketing are divided into four large blocks (see Cost items for current marketing activities).
How to determine marketing budget
Cost items for current marketing activities
1. Costs of traditional advertising.
This is the placement of paid information about a company, its products or services in the media, as well as the use of various advertising media for these purposes. Typically this includes TV costs advertising, advertising on the radio and in the press.
2. Costs of direct marketing (direct marketing).
These costs consist of the following:
- sales through a network of distributors;
- postal, electronic and fax distribution;
- telemarketing;
- courier delivery;
- catalog sales.
3. Sales promotion costs.
These expenses provide:
- organizing the work of showrooms;
- free distribution of demo samples;
- presentation of new types of products (or new trademark);
- reduction in product prices;
- holding sales, competitions, lotteries, coupon discounts;
- participation in exhibitions and fairs, organizing company visits, etc.
4. Research costs
- market,
- competitors,
- consumers.
Sometimes the marketing goal is formulated rather vaguely: “So that people know about us...” The task can be specified (made quantitatively measurable) by answering questions How many questions:
- Who should find out? Determined target audience, its size.
- What specifically should consumers know? The object is being installed advertising(products, services, new items, company image, terms of cooperation, unique selling proposition, etc.).
- What will this give us and in what time period? It is clarified how long it will take to solve the problem and how it relates to sales volumes and profits.
In my opinion, for planning budget all goals must be quantifiable, otherwise it is impossible to evaluate achievements or allocate resources. Typically, slogans are formulated rather than goals; in 90% of cases, marketing objectives sound like “we’ll give advertising", "let's hold an action." Instead, you need to plan to achieve specific goals (for example, attracting 1,000 new customers using advertising in the specialized press).
Speaks General manager
Vladimir Kiselev | General Director of JSC "SHERP Company", Moscow
From my point of view, all expenses associated with promoting a product and brand are marketing expenses. Therefore we are in budget for marketing we include expenses for the following events and activities:
- marketing research;
- advertising and PR;
- promotions (presentations, seminars, conferences, etc.);
- working with agents;
- providing sales support tools (website, booklets, souvenir products etc.);
- direct sales.
When forming marketing budget We are goal-oriented first and foremost. The first question: “What do we want to achieve?” (goal setting and justification). Second: “How to achieve this?” ( marketing planning, identification of specific activities to achieve goals). Third: " How many is it worth it?
Now ours main goal– bring to market in principle new product. For this we are ready spend so many, How many will be necessary.
Step 2: Select a method
Determination methods budget for marketing are given in Table 1. The most common method is to determine budget as a percentage of the expected (or achieved) sales volume or profit received. This method is quite simple and at the same time accurately reflects the main goal of tactical marketing - increasing sales. Also very popular are methods of planning “on the residual principle” and in comparison with the costs of the leader or closest competitor. We can cite a case as an example. Thus, one diversified company, which also provides advertising services, three years in a row determined budget for marketing in the amount of 5% of annual turnover, explaining this by the fact that in the advertising law 5% of turnover is allocated to cost.
Case Study
The Toyota concern is going to spend almost half a billion euros to promote Lexus cars in Europe. Through aggressive marketing, the Japanese hope through not How many years to sell up to 100,000 cars per year (now - 20,000), that is, increase sales volumes five times. Marketing costs will also increase fivefold, by 150–170 million euros per year.
All of these methods of determining marketing costs are logical and consistent, but they are best used in combination.
At integrated approach to estimate marketing costs, you can use all five methods (similar to estimating the value of companies, when three independent methods are used).
Determination methods marketing budget. Table 1
Methods |
Description
|
According to the residual principle
|
When planning, they proceed from the amount remaining after the distribution of funds to higher priority areas
|
Parity with competitors
|
The approximate amount of marketing expenses of a competitor is taken as a basis.
|
|
|
Depending on the goals and objectives of the company in the field of marketing
|
From sales
|
Budget determined as a percentage of existing or planned sales volumes
|
From the achieved level
|
Increase or decrease in costs depending on the results of the past period
|
Step 3. Determining the amount of costs(*)
Western marketers believe that the share of marketing costs in the cost of traditional goods in developed countries is about 25%, and of new products – up to 70%. Taking into account profitability, we will get a basic share of marketing costs for traditional products in the range of 10-15% of sales revenue. In Russia, the share of marketing costs should be considered in the amount of 1 to 5%, that is, on average, 3% of revenue. This is, of course, an approximate figure, but it can be taken as a base.
In preparation marketing According to the plan, marketing costs for the previous year are correlated with the sales results obtained. Depending on the indicators of the previous period and taking into account the changes that have occurred in the market over the year, we set tasks that need to be solved in the new year (rebranding, introducing a new service to the market, occupying an existing market niche or strengthening existing positions). Size budget usually amounts to 3–5% of turnover.
How marketing costs vary depending on your goals. Table 2
Indicators |
Implementation
|
|
Maturity
|
|
Marketing Goals
|
1. Attracting customer attention to a new product or service
2. Formation of the image of a new product or service
|
1. Sales expansion
2. Expansion of product groups
3. Building brand loyalty
|
1. Maintaining the distinctive benefits of the product or service
2. Defending market share
3. Finding new niches, new ways to consume goods or services
|
1. Preventing a drop in demand
2. Recovery of sales volume
3. Maintaining sales profitability
|
Sales volume
|
|
Fast growth
|
Stability, slowing growth
|
Reduction
|
Competition
|
Absent or insignificant
|
Moderate
|
|
Minor
|
|
|
Negative
|
Increasing
|
Contracting
|
Rapidly declining, no profit, losses
|
Marketing costs
|
Extremely tall, growing
|
High, stable
|
Contracting
|
|
Correction factor
|
|
|
|
|
How marketing costs vary by industry. Table 3
Depending on the specifics of your company’s activities, the given algorithm for determining marketing budget can be supplemented and clarified by marketers. For example, marketing budget companies operating in the service sector will be much larger than those of enterprises selling goods: in the first case, it ranges from 30 to 50% (and higher) based on the company’s turnover. Table 4 shows coefficients showing differences in marketing costs in industrial and consumer markets.
How marketing costs vary by market type. Table 4
Step 4: Cost Allocation
Distribution marketing budget by main cost items depends on the industry in which your company operates, the strategy for solving marketing problems and the type of market.
Costs for advertising some companies
If your business is not built on any one type of marketing (you do not, for example, rely exclusively on distribution through catalogues), costs can be distributed taking into account the following coefficients (Table 5).
Distribution of marketing costs by main items. Table 5
Grade efficiency marketing costs
The final indicator of marketing activities is the company's turnover or sales revenue. But, for example, in the initial stages of introducing a product to the market, it is more important to achieve a certain awareness of consumers and create a favorable image of the product (or service). Therefore, at each individual stage for evaluation efficiency marketing costs, it is advisable to use different indicators, depending on previously formulated (quantitatively measured) goals. The goal itself should serve as the main indicator efficiency: we reached the goal, which means we effectively planned costs and implemented the plan; if we didn’t achieve it, we need adjustments.
During development and approval marketing budget our marketers work very closely with financial department. Marketing specialists write a plan, which is then agreed upon with financiers. Marketing budget is based on a percentage of the company’s turnover: a fixed percentage is allocated for the department’s activities (from 3 to 5% depending on the tasks for the year), then marketers plan internal redistribution of funds according to cost items (attracting and retaining customers, traditional advertising in the regions, marketing promotions). If previous years were successful and we do not see the need to increase budget, the allocated percentage of turnover remains the same. Our company operates in a developing market, and in proportion to the growth in turnover, marketing costs also increase: if last year I had a turnover of one million, and this year I sold two million worth of products, then budget doubles.
In a situation where the percentage of turnover remains the same as in the previous year, the task of the marketing department is to increase efficiency costs: having spent the same 10 thousand, the department must provide not 100 thousand customer calls (as last year), but 120. And if last year 22% of first-time clients ordered windows, then this year this figure should increase to 30% . How they will do this is determined by the director of marketing and advertising. He analyzes the work of the department, draws conclusions about successes and shortcomings, decides what is worth repeating and what needs to be done better. I believe that the marketing department should work more efficiently every year, since experience is gained and it is already clear from practice how best to proceed. If my marketers spend the same amount and give the same volume of orders, they are worthless.
The marketing budget is the costs of market research (market research, medium- and long-term), ensuring the competitiveness of goods, information communication with customers (advertising, sales promotion, participation in exhibitions, fairs, etc.), organizing product distribution and sales network.
Funds for all this are taken from profits, and the amount of these expenses is reduced. But, on the other hand, in our time, without marketing costs, it is impossible to sell such a quantity of goods to return the costs of research papers, production of goods and also making a profit. Therefore, allocating funds for marketing is a solution to multi-vector problems, the impact of which on marketing is even difficult to determine. Therefore, when determining marketing funds, they often rely on traditions, past experience, intuition, as well as analysis of competitors’ marketing costs.
To estimate the amount of marketing expenses, the influence of the following factors is analyzed:
S- sales volume in pieces;
W- list price;
IN- transport, commission and other expenses for the sale of a unit of goods;
A- costs of producing a unit of goods that are not related to marketing, but depend on the volume of production;
F- constant production losses not related to marketing and independent of production and sales volumes;
D- costs of product promotion (sales promotion).
Let's connect all these indicators in the profit equation. We get the following equation:
But the formula does not take into account the rate of profit, which, in turn, depends on the size of the market share.
From the profit equation, it follows that advertising and promotion costs should also increase in accordance with the extent to which the company penetrates an increasingly larger part of the market. It is believed that exporters spend 2-5% of the amount of their exports on advertising in importing countries.
Sometimes the analogy method is used to determine the necessary marketing costs. It is known, for example, that in the USA the costs of developing and launching a new product on the market are distributed as follows: basic research 3-6% of the estimated costs are allocated for applied development - 7-8% for preparation technological equipment- 40-60%, for arrangement serial production- 5-16%; for sales organization (advertising, sales promotion, organization of product distribution and sales network) - 10-27%.
IN modern world Marketing costs are constantly rising.
Every company should have highly qualified specialists who can correctly calculate the marketing budget in order not only not to lose, but also to expand market share. All company expenses for marketing activities are marketing expenses, which are carried out in three directions: for the creation and maintenance of a marketing department, for developing a strategy (the general direction of development for a certain period), and tactical marketing expenses.
Strategic marketing is an active marketing process with a long-term planning horizon, aimed at exceeding market averages through the systematic implementation of a policy of creating goods and services that provide consumers with more valuable benefits than competitors.
Strategic marketing directs a company toward economic opportunities that are tailored to its resources and provide the potential for growth and profitability.
The task of strategic marketing is to clarify the company’s mission, develop goals, and form strategic development, ensuring a balanced structure of the company’s product portfolio.
Tactical marketing is a type of marketing that is based on the active process of finding and retaining customers, promoting products with a short-term planning horizon, aimed at an existing market. This is a classic commercial process of obtaining a given sales volume through the use of tactical measures (actions in accordance with a specific situation) related to marketing, the buyer, the product, its price, promotion of the product and bringing it to the consumer.
The largest amount of costs falls on tactical marketing, that is, on ongoing marketing activities.
At enterprises, a distinction is made between fixed marketing expenses (constant) and those that will change due to changes in sales volumes of goods. But it is better to calculate the total distribution costs directly in the value of sales of units of goods. They can then be counted as a percentage of income.
Fixed marketing expenses during planning period- This:
Wages sales staff and the costs of its support;
Production costs and costs of major advertising campaigns;
Marketing staff costs
Expenses for sales promotion materials (sales aids) retail outlets, distribution costs);
Variable Marketing Costs:
Sales commissions paid to sales personnel, brokers, or representatives of the manufacturer;
Sales bonuses that depend on sales targets;
Discounts from invoice prices and for achieved results of current sales;
Prepayment funds (if included in the sales promotion budget);
When the marketing budget considers expenses as both fixed and variable, the budget will be more objective. It is also important to consider that the short-term risks associated with fixed marketing costs are always greater than those associated with variable marketing costs. If, as a result of market analysis or production process Marketers come to the conclusion that factors beyond their control (actions of competitors, production cuts) clearly affect income; they can reduce risks by including more variables and more fixed costs in the marketing budget.
Winning calls that change in proportion to income are sales commissions on remuneration. Therefore, any sales commissions should be included in variable distribution costs. To confirm this, the following example can be given. The Torchin company, which sells ketchup, spends 1 million UAH. per year for the maintenance of sales personnel working with networks grocery stores and with wholesalers. The reseller offers to do the same sales work for a 5% commission.
With an income of 10 million IRN:
total variable distribution costs = 10 million UAH. 5% = 0500000 UAH.
With an income of 20 million UAH:
total variable distribution costs = 20 million UAH. 5% = 1 million UAH.
If the enterprise’s income is less than UAH 10 million, then the services of a reseller will be less than the payment of its own sales personnel.
It should also be noted that fixed costs are easier to calculate than variable ones. Information about fixed costs can be obtained from payroll records, financial statements, and lease documents. Difficulties arise when calculating variable costs. Often variable expenses owe a given percentage of income. Then they will change with the change in the number of units sold. And it happens that variable costs relate only to part of the total sales volume, that is, the costs are constant until a certain stage (phased).
It is important that when developing a marketing budget, it is determined how much of the expenses to allocate for the current period and which to gradually spend in future periods.
A company's level of marketing expenditure is often used for comparison with other businesses, so these expenses are considered as a percentage of sales, or a share of sales. Based on this share, they can conclude how actively the company is engaged in marketing. The indicator “marketing costs” (%) = marketing costs (UAH) income (RUB).
Advertising expenses can also be determined as a percentage of sales volume.
A special form of distribution costs is “location deductions”. Very often, deductions occur when new shipments of goods are delivered to retailers and they provide them with space for these goods in warehouses and stores. Such deductions can be one-time cash payments or special discounts.
Understanding the difference between constants and variable costs appeal helps a firm consider the relative risks associated with alternative distribution strategies.
In general, strategies that involve variable costs are less risky.
Marketing product policy involves the selection of target markets, the development and justification of a set of marketing activities, the implementation of these activities and monitoring their implementation.
In the selected target markets, demand volumes, segmentation and selection of target segments, as well as product positioning are determined.
A set of marketing activities should cover strategy, tactics, product content pricing policy, selection of promotion and sales promotion methods. Product marketing policy also extends to the sphere of direct trading activities: market analysis, research in the field of market pricing, influence on the level of demand, establishing communications.
Marketing research is ordered by large commodity producers and wholesalers (distributors). There are certain research standards, according to which the company that orders must provide the contractor with technical specifications and the subject of the tasks, the necessary information about the company, and pay for the work performed.
The contractor’s obligations include conducting research within the agreed time frame and in accordance with the program and respecting intellectual property rights.
Based on the results of the study, a report is drawn up for the customer.
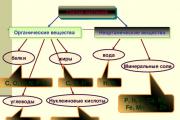
Below is a list of marketing expenses:
To conduct marketing market research, competitive advantages, prospects for the development of the product range;
For business trips of employees to exhibitions;
Cost of product samples provided to customers free of charge;
For the development and production of sketches of labels and packaging;
For the design of lighting, transport, outdoor advertising;
To carry out other sales activities.
Sales expenses of a current nature are recorded in the balance sheet account “Sales expenses”.
Determining marketing costs is a rather difficult task, because:
- · marketing costs ensure the process of selling goods;
- · marketing costs are of an investment nature and can bring income in the near future;
- · financial planning marketing costs are carried out when developing appropriate budgets (research, communication policy, etc.).
When determining marketing costs, the following methods are widely used:
- · “top-down” - first the total amount of costs is calculated, and then this amount is distributed to individual marketing activities. In this case, the approaches presented in Fig. 1 can be applied. 7.1;
- · “bottom-up” - first, the costs of individual marketing activities are calculated, and then these values are summed up using the cost calculation method using the relevant norms and standards (calculations are carried out by the enterprise’s marketing service or by external experts on a contractual basis).
Rice.
Costs for individual marketing activities are divided into fixed and variable.
Fixed marketing costs are the costs necessary to constantly maintain the functioning of the marketing system at the enterprise. They include costs for:
- · maintenance of marketing service personnel (salaries, travel expenses, etc.);
- · systematic marketing research;
- · creation of a bank marketing information for enterprise management;
- · financing of work aimed at improving the product range of the enterprise.
Variable marketing costs are costs associated with changes in the market situation and market conditions, the adoption of new strategic and tactical decisions.
The marketing service prepares cost estimates in the following areas:
- · costs of marketing research;
- · costs of developing new products;
- · distribution costs;
- · promotion costs.
A modern method of planning marketing costs is the method of marginal marketing budgets, based on the fact that the elasticity of consumer response varies depending on the intensity of marketing efforts. At the same time, the expenditure of funds on the use of each element of the marketing mix is determined, which leads to the best results (the greatest magnitude of effect).
- 1. The salary of marketing service employees will be 15,000 rubles.
- 2. The number of bets will be equal to 1.
- 3. The employee bonus is 20% of the salary.
- 4. The salary will be charged 30% of the regional coefficient, 20% of the northern coefficient.
That is, labor costs will be: 1*15000+3000+9000=27000 rubles.
5. From wages employees will contribute 30.2% to social insurance.
Insurance premiums:
27000*30.2%=8154 rub.
The costs of maintaining and operating the equipment will be:
35154*50%=17577 rub.
Thus, the monthly cost of maintaining the marketing service is
27000+8154+17577=52731 rub. or 52,731 thousand rubles.
In addition to the costs of maintaining the marketing service, there are costs for marketing research, which amount to 0.3% of income. Thus, 0.3% of revenue goes to collecting and analyzing data that is required for marketing activities.
Using the presented minimum marketing costs of 48,850.42 thousand rubles at the Lot-Mebel LLC enterprise, the enterprise will be able to conduct market research, identify customer preferences, improve product sales and enter the world market.
Marketing costs in each month may be different; there is no need to conduct an in-depth analysis of the market every month, since with a full and in-depth analysis at the first stage of the study, it is possible to express a stable pattern of development in the industry, in the preferences of buyers. The effectiveness of conducting in-depth market analysis is once every six months or a year.
In addition to allocating the costs of conducting market research, it is necessary to annually review the costs of maintaining the marketing service. Bonus percentages may vary depending on the stability of the economic condition of the enterprise and the performance of department employees.
In previous articles of our magazine dedicated to marketing function, we touched on a number of organizational issues: the structure of the marketing service, job descriptions of employees of marketing departments, etc. The next topic in turn is determining marketing costs. We included this topic in this issue based on the following arguments. Most firms are now experiencing resource constraints. There may, of course, be exceptions, but the dominant austerity of financial resources exists. In this situation, it becomes quite possible to shift marketing costs to “later”, partly due to a lack of understanding of the importance of this management function, partly due to a lack of knowledge in the field of maneuvering resources within the marketing function. In this regard, when preparing an article for this issue, we asked our clients to send us their marketing budgets broken down by item. The results of the generalizations we have made, as well as additions from statistics from the American Bank Marketing Association, the American Apparel Manufacturers Association, and the American Retail Merchants Association, are before you. Perhaps some cost items may seem irrelevant to you in your circumstances. It's OK. Just put "0" against these lines for now, but rest assured that sooner or later they will be useful to you.
So, marketing is aimed at creating and maintaining a positive image of the organization, maximizing the use of its resources to identify, promote and satisfy market needs for products and services on a profitable basis. In this context, from the standpoint of determining cost items, 4 blocks can be distinguished within the marketing function:
A. Advertising. Transfer of certain information through media selected by the client for: a) motivating the customer to purchase or use a product-service that provides benefits, guarantees or satisfaction to the user,
b) transfer of information aimed at strengthening the reputation or position of the advertiser.
B. Marketing research. Using various methods and tools on an ongoing and systematic basis to analyze information related to:
Who are existing and potential clients?
Geography of client placement.
What products and/or services does the client want and which ones does he really need?
Where the client prefers to receive services or how and when they should be provided.
What are the conditions of competition?
- Satisfying the needs of existing or potential clients or their wishes.
- Ratings of existing or potential customers regarding products or services provided, personnel, policies and procedures, etc.
B. Public Relations. A permanent and ongoing program of activities designed to involve a firm in the social, cultural, educational, environmental and economic life of a region or larger administrative entity (for example, a country).
D. sales promotion. A set of actions to enhance the effectiveness of advertising and customer contact programs by increasing awareness and knowledge of products or services at the point of sale.
We present these well-known truths with one single purpose - to connect the upcoming lists of costs with the above marketing blocks. Now let's move on to cost items.
7. Acquiring space at trade shows, fairs, etc.
15. Costs for photographs and payment for models participating in advertising.
17. Posters, displays, etc., placed within the company for advertising purposes.
MARKETING RESEARCH COSTS
1. Research on advertising pre-testing and advertising effectiveness.
2. Payment for marketing research consultants.
3. Research related to the introduction of new products and services.
4. Research related to the company's image; public opinion research.
5. Quarterly, semi-annual and annual sample market research for penetration and perception.
6. Testing and evaluation of sales promotion activities.
Ultimately, all costs are aimed at conducting research on the potential of new products and services, market share, the selection of branches and affiliates, the image of the company, the effectiveness of advertising and preliminary testing of proposed public relations projects.
PUBLIC RELATIONS COSTS
2. Celebrating anniversaries and significant dates.
4. Awards given in charitable events.
5. Calendars.
6. Greeting cards.
7. Financing of events carried out by municipal authorities.
8. Donations and subsidies.
9. Production of displays for the needs of municipal authorities.
10. Payment of public relations consultants.
11. Payment for special events offered to the public.
12. Gifts and souvenirs with the organization’s logo.
14. Letters of gratitude clients for agreeing to do business with the company, various types of congratulations and their mailing.
15. Production of geographical maps with the company logo and its location.
16. Costs of holding an open house day for the company.
17. Sponsoring of creative and sports groups and cultural/sports events.
18. Press conferences.
19. Costs of scholarships.
20. Costs of weather and time systems for installation in public places without a company logo.
21. Costs of external speech writers.
23. Development of a trademark or company logo.
COSTS FOR SALES PROMOTION (a separate group of costs aimed at expanding knowledge about the company’s products and services both externally and internally).
1. Audiovisual materials, including slides, audio and video tapes for demonstration during speeches related to the sale of products and services.
2. Production of items (banners, boxes, etc.) for use at points of sale of products and services.
3. Souvenirs for clients starting business with the company.
4. Prizes or bonuses for employees who attract new clients.
5. Letters related to increasing sales volumes and their mailing.
6. Training of personnel related to the sale of products and services.
7. Organizing meetings with new clients