In this article we will look at what FMCG products are and what are the specifics of this area. Surely you have come across the abbreviation FMCG (fmsji) and for good reason. This is an abbreviation for consumer goods and the literal translation (fast moving consumer goods) means fast-moving consumer goods. All products that people buy regularly and very often can be classified as FMCG, and this creates very strong competition in the developed and technological market for this product.
FMCG companies themselves are worthy employers with good wages and low staff turnover. . The market itself is quite stable and promising.
FMCG products
What specific groups of consumer goods belong to FMCG?
- Alcohol;
- Food;
- Tobacco products;
- Household chemicals.
Although there are many more varieties of consumer goods, it should be noted that FMCG products: meat, bread, cigarettes, matches, condoms, turn around much faster than: watches, glasses, phones, etc. This means that the buyer fast goods a habit is formed of buying these goods in a certain place and with a certain cyclicity. Therefore, technologies for selling FMCG goods are developing very quickly, which is reflected in the range, convenience and accessibility for the end buyer.
The FMCG product group is characterized by some marketing features:
- Low price tag for goods with low profitability. The low price tag forces a private buyer to purchase a product almost without hesitation, making a decision on his own without consultation and help from the seller.
- The turnover is very high, so it is necessary to carefully consider the supply of goods and the filling of shelves in the store.
- The cyclical nature of purchases is high, since bread, tea, washing powder (products with a short life cycle) quickly run out and force a person to make purchases again and again.
Features of FMCG marketing
The main task of FMCG marketing is to create a stable and conscious need among the consumer, but the consumer, in turn, should give preference to the brand that could interest him with its range, packaging and price. You, as a consumer, may not understand shampoos, but you will still choose a product from a certain brand. The manufacturer took care of this in advance.
You have probably come across the abbreviation in specialized literature and on the Internet FMCG What this is is usually not explained there. After all, it is assumed that the reader already knows most of the concepts and has basic knowledge. If this is not the case, it is worth expanding your knowledge base with more mundane data before starting to delve into the details.
What are we even talking about?
First, you need to understand the abbreviation itself, what words are hidden behind these 4 letters? . Actually, the situation did not become too clear after this clarification. These are products that we use regularly. In Soviet literature there is one very good word that was used as the name of all products of this plan - consumer goods.
Perhaps in the 80s and 90s this word acquired a slightly different emotional connotation, but initially it meant consumer goods. Main criteria:
- Interest of wide sections of the population.
- Frequent acquisition, almost automatically.
- Willingness to spend money without even realizing it.
- Fast implementation and short shelf life.
- Low markup.

What is the FMCG market?
All this created special conditions, which form the consumer goods market:
- Availability of large chain stores distributing FMCG goods.
- High level of competition.
- Numerous promotions to attract the attention of buyers and sell goods that may expire in the near future.
- Using all possible marketing techniques.
- Good profits are due to the regularity of purchases.
There are competitors in any business, but there are especially many of them in this one. It’s easy to make sure, go outside and walk to the nearest supermarket or shopping and entertainment center. The walk will take a few minutes, and several more such establishments will be visible on the horizon. And this even in small towns, let alone the capital or regional centers.
At the same time, each store is trying to win its share of the audience.
After all, the most important thing is that visitors don’t even have doubts about which store to go to on the weekend for shopping for the whole week. Usually, the location of the outlet also influences success. The closer to densely populated areas and transport interchanges, the more city residents are covered by one large store.

Chain stores versus small distribution points.
Why large stores? Let's consider table of differences between chain retail and small sales points:
|
Supermarkets
|
Small shops
|
|
Bulk purchases of goods, often at better prices.
|
Small batches, rarely when there is access directly to the manufacturer.
|
|
The absence of intermediaries increases the profit level of store owners.
|
The presence of several more links in the repurchase chain.
|
|
The ability to quickly sell stale goods through high-profile promotions.
|
A fast moving product can turn into a quick loss.
|
|
Solid capital allows you to minimize risks even in the event of loss of part of the production.
|
Trading "from batch to batch". Each time the owner must worry about the possibility of selling the product.
|
|
Using marketing techniques, creating separate zones for goods.
|
Due to the small footage, this becomes a difficult task.
|
In this comparison, larger firms always win; small private traders find it difficult to survive in the market. Large trading companies can afford low prices by optimizing logistics costs and through discounts provided by suppliers for large volumes of purchases.
But this in no way means that the entire market is captured by soulless hypermarkets, in which marketing specialists manipulate the mass consciousness of buyers. The first floors of houses will be used for a long time as small shops where you can shop and exchange a few words with the seller.
A matter of habit and proximity to home, walking distance. Sometimes such points are located right in your home.

FMCG companies, what is it?
So far, FMCG products have been named only in the abstract, without any specifics. Time to change things up and introduce you to major global brands
:
- Coca-cola.
- Nestle.
- Pepsi.
- Henkel.
- Danone.
- Colgate.
You have used the products of the listed companies more than once. If you go to the kitchen or bathroom now, you will probably find several units of goods from these manufacturers there.
What allows such corporations to increase the pace and volume of sales:
- World name
- Universal recognition
- Billions of dollars in advertising budgets.
Typically, companies have contracts for several years in advance with large chain stores. This helps the former to solve the sales problem, and the latter to fill the rows of shelves and attract customers. The markup, as already mentioned, is minimal.
Firms simply cannot afford to raise prices; this will not only lead to increased discontent among the population, but will also ruin multimillion-dollar profits.
Only one factor saves: in personal hygiene products and food products people need regularly. Nobody in their right mind will cut this line of family budget expenses. At the same time, the brand does not have to have a particularly wide audience. If hobbyists are willing to buy a product daily, this will compensate for their low quantity.

FMCG sales - what is it?
You've probably noticed that your favorite hypermarket constantly changes the location of goods. And the most expensive products lie next to the bread, the smell of fresh baked goods does its job. The calculation of these manipulations is extremely simple:
- The visitor will not follow the planned route, but will walk around most of the store.
- He will come across many products that he did not even intend to buy.
- A momentary desire will at least a couple of times override the original plan.
- Pleasant smells, lighting and arrangement of items will also encourage the desire to add a few extra items to your cart.
It cannot be said that chain stores are directly forced to resort to such methods. Quicker, they have the opportunity to “squeeze” as much money as possible out of the input, selling him the maximum amount of goods from the sales floor. It would be stupid not to take advantage of this opportunity.
And since the shelf life of everyday grocery products rarely exceeds several weeks, it means that the buyer guaranteed to return, and in the near future. All that remains is to create a positive image of the enterprise so that no one is offended and gratefully carries their money next time.

The consumer society is a fact.
In fact, there is nothing to reproach both FMCG companies and their distributors. The consumer society has long been formed, including in our country. All efforts of the majority of the population are aimed at earning and spending as much money as possible. Even if there is no need for these expenses, just another try:
- Compensate for past failures.
- Show yourself that you can do it.
- The desire to assert oneself.
The statements, although they seem far from consumer goods, actually relate to almost all areas of our lives. But still, manufacturers can be thanked for providing quality products at low prices. And thanks to supermarkets, we can choose and purchase almost anything with a minimal markup.
There was no such diversity before, but now the only problem may arise with financial solvency.
New knowledge regarding FMCG, what it is and how these products are sold is a useful thing. But this will not affect your future life in any way; you will not stop visiting the nearest large store and buying your favorite products there. By the way, scandals periodically emerge regarding the use of child or even slave labor in production.
Video about FMCG
This material opens a series of practical articles on increasing the profits of FMCG market enterprises through increasing the efficiency of marketing, development and sales services. These materials will be relevant for enterprises and other sectors, since the FMCG market is one of the most dynamic and highly competitive, and with the most developed marketing and business development technologies.
Introduction
The efficiency of enterprises in the FMCG (Fast Moving Consumer Goods) market depends, in a key way, on the distribution (representation) and disposal of goods from retail outlets.
Any marketing activity will be nullified if the product is not on the store shelves or there is a situation of “overstocking” (when a type of distribution channel has several times more inventory than it is able to sell per unit of time - especially true for goods with long shelf life) distribution channel.
In the current conditions of limited marketing financing, working with the trade channel is one of the most effective tools, capable of delivering results at minimal cost compared to other communication tools and in a short time.
In addition, ATL activity (carrying out events aimed at indirect contact with the target audience, implies advertising in the press, transport, television, radio, outdoor advertising) must be carried out at a retail representation level of at least 20%.
Communication activities aimed at interacting with end consumers must be carried out at a level of product representation in retail outlets reaching at least 20%, since otherwise the sale of promotions may lead to negative consequences. It is worth noting some of them.
- A brand whose promotion program has been launched, but is not on store shelves, may be associated by the consumer with a brand that is constantly absent from retail outlets. The consumer decision-making model for purchasing in the FMCG market is such that, in search of the product (brand) he needs, he turns to a maximum of three to five stores (the minimum distribution level should be at least 20%).
- The effectiveness of promotion programs is directly proportional to the quantitative representation of products. A low level of distribution entails a direct reduction in the effectiveness of promotions implemented to attract end consumers.
Thus, activities aimed at ensuring brand representation in retail outlets are key in the brand promotion system. The ongoing trade marketing programs are of particular importance for a number of sectors of the FMCG market (for example, alcohol and tobacco), where the range of communication tools is legally limited. To achieve the greatest efficiency when introducing a new product to the market, promotions should primarily be aimed at interacting with that distribution link that directly affects the product’s presence in the retail sector.
FMCG trade marketing system
Events trade marketing is a system in which a participant in the commodity distribution route is provided with appropriate financial or other motivation for achieving a certain KPI. The goals of these events can be both short-term (information and increasing sales) and structural (building loyalty), including:
- increase in sales volume due to increased distribution and expansion of the product line;
- increasing the level of representation due to increased sales volumes;
- familiarization with products by distribution channel participants, receiving feedback;
- expert assessment of product items that are in greatest demand, carried out by persons making purchasing decisions (if it follows from the terms of the promotion that the assortment can be formed by the person responsible for purchasing products included in certain product items);
- increasing the loyalty of partners - participants in the distribution channel (for entering retail chains, creating greater commitment compared to loyalty to other companies / brands, creating better trading conditions);
- attracting consumer attention to products through expanded display and placement of products in attractive places;
- attracting the attention of representatives of companies that do not sell these products who make decisions about the purchase of goods, by monitoring the display in competitors' stores (about 30% of non-chain retail companies monitor other retail outlets, for chain retail this figure is close to 90%);
- increasing the number of positions in the assortment matrix (distributor or final retail outlet);
- improving the quality of display.
The trade marketing model in the FMCG market is shown in the figure
* MPP – comprehensive marketing promotion program
A significant part of market operating companies, when carrying out trade marketing activities, direct their efforts to one, maximum two links of the Chamber of Commerce and Industry, and very often this is only the first link - which does not communicate with customers in retail outlets (is not responsible for placing goods on shelves). Thus, when motivating those responsible for purchasing products (merchandise experts), there is no promotion of incentives for sellers in retail stores, who can directly influence the consumer’s purchasing decision and ensure the disposal of goods.
And here a situation may arise that will negatively affect the results of promotions and sales in general - oversaturation of distribution channels and further sales of products at reduced prices, which also entails a subsequent drop in sales. The risk of this situation especially increases when only one (first) link of the distribution channel is motivated - a large wholesale company without taking into account and controlling further product distribution. The solution to this problem for the manufacturer is to focus the promotion not on the dealer himself, but on his clients (smaller wholesale companies, subdealers, etc.). Next, the author's trade marketing program will be considered - the motivation of all links of the commodity distribution path when introducing a new brand to the market, which has proven its effectiveness in practice.
In addition, there is a risk when conducting trade marketing programs, which is associated with an insufficient level of control. When stimulating the distributor's sales staff - the head of the sales department, sales managers, sales representatives - a situation very often arises when the funds from the motivation fund transferred by the organizers of the promotion simply do not reach the specified employees, i.e. those who directly achieved their goals. This fact, of course, has a very negative impact on both the effectiveness of the action itself and the reputation of its organizers.
10 principles of effective trade marketing campaign.
- Setting goals. The goals of the action at the stage of its preparation must be clearly formulated, their results must be measurable, based on the feasibility of achievement and an exact time frame (formulation of goals in SMART format).
- Prizes and motivation fund. It is necessary to determine gift options based on values target audience(managers, merchandisers, sellers), i.e. the prize should be interesting and useful. In addition, it is important to understand the likelihood of actually receiving a gift. The promotion will not be effective if, for example, when holding a competition for merchandisers of retail stores, a single car is raffled off as a prize. On the contrary, the teapot either mobile phone, the possibility of obtaining which will be obvious, will become an incentive to achieve the desired result.
- Visualization. A clear reflection of the terms of the promotion and prizes is one of the key conditions for organizing the program. On advertising and information media it is necessary to depict gifts and characterize the terms of the promotion. Maximum use should be made of placement opportunities to convey information to the target group. Information should be published on the company’s website, internal corporate portals(in the case of a motivational program for managers).
- Winner's reward ceremony. It must take place publicly, with the involvement of the maximum number of participants in the action. This is necessary for them to understand that victory in the competition is real and achievable. Publicity in this case will also act as an informational reason for further PR campaigns.
- Control. It is necessary to monitor the process of implementing the program, remind about the progress of its implementation and intermediate results (as practice shows, when conducting such events, for example, for the sales staff of a distributor, employees forget about the program one to two weeks after the launch). Prizes must be awarded directly by representatives of the event organizer in order to prevent a situation in which the gift does not reach the recipient.
- Creation of an information and analytical base. The goal here is operational control of measurable indicators (number active clients, rate of product disposal, width of the product line, etc.), the progress of the program and the movement of goods before they are retired from retail. To plan targets, it is necessary to conduct an audit of the distributor's sales.
- Brief and accessible presentation of the terms of the promotion.“Five sentences on one page” - this is how you can designate the format for presenting information about the conditions for the implementation of the event, prizes, the mechanism for holding and receiving gifts. Information should be simple to understand, easy to remember and not difficult to interpret.
- Control of product disposal from retail. When carrying out promotions aimed at stimulating the efficiency of distributors, it is necessary to control the movement of goods in order to avoid a situation of increasing warehouse stocks in this period. Control is carried out by analyzing the distributor's shipments to its customers.
- Education. When organizing training for the distributor's sales staff during a promotion, introducing a merchandising standard in a retail company through sales representatives, it is necessary to focus on the rules and methods of selling your products, and not on the general principles of sales and merchandising.
- Complexity. In practice, the best performance indicators are inherent in projects with a comprehensive impact on the commodity distribution route along the “manufacturer-consumer” chain. In this case, the involvement of all participants in the distribution channel increases, and the risk of its oversaturation decreases. In addition, campaign costs are reduced.
Integrated trade marketing campaign.
I developed my own trade marketing technology, which made it possible to solve marketing problems using less resources and reducing the risk of standard negative situations arising from trade marketing activity (channel overpacking, low level of control, etc.).
I have been using this technology since 2006 and have proven its effectiveness in practice. I will illustrate the technology and results of the project using the example of a company that produces grocery products.
When promoting an umbrella brand (four product groups: cereal flakes, cereals, ready-made breakfasts, gourmet flour; a total of 23 assortment items; price segment - “medium+”) in the market of one of the federal districts, I, as Director of the Marketing Department, implemented a comprehensive program working with the distribution channel. Its activities were an integral part and foundation of a larger promotion program, which included the stages shown in Fig. 2.

Rice. 1. Stages of the promotion program
It was decided to abandon the use of direct price promotion methods (discounts, cost reductions, special payment terms), and provide direct bonuses to persons responsible for achieving target indicators when promoting products in the trading channel.
Program targets
Structure retail in the program area were 70% of non-chain retail outlets and 30% of chain retail stores. Before the start of the program, we managed to agree with three distribution companies that provide direct delivery of goods to non-chain retail outlets on the distribution of products during the implementation of the promotional program. Before it began, an audit of the distributor's sales was carried out - the size of the active customer base, the structure taking into account the directions (retail, chains, wholesale, HoReCa) in a certain period of time (Table 1).
Table 1. Table for conducting a distributor sales audit
Data from the distributor's sales audit were the starting point for the formation of program target indicators, determined based on the number of stores in which the product should be presented (active customer base - AKB), the number of assortment items in one outlet (width of the assortment line - SHL) and speed, at which each product will be sold within a month (disposal rate - SV).
Thus, an individual sales and promotion plan was developed for the three companies. The distribution plan indicators (SL and AKB) were developed as a result of an agreement between the supplier company and the distributor. It is worth noting that SV is an indicator that depends on many factors: price levels, awareness and purchasing behavior, seasonality, and quality of display.
Methodological basis and progress of the program implementation
The promotion program under consideration included three main blocks; the parameters and conditions for its implementation were specified in the agreement concluded with the distributor (Fig. 3).

Rice. 3. Main blocks of the promotion program
Motivation of the distributor's sales staff
Motivation of sales personnel (head of the sales department, sales representatives) was carried out through the payment of bonuses for fulfilling distribution and sales plans.
The head of the sales department received a bonus for implementing the final distribution plan (2,500 rubles) and the sales plan (2,500 rubles) monthly during the program period.
A sales and distribution plan was developed for each sales representative. Based on their performance results, these employees were paid a monthly bonus (1,700 rubles) for achieving a specific target. Posters describing the terms of the promotion and a description of the incentive fund were placed in the company's offices, and corresponding information modules were available on corporate portals.
To eliminate the possibility of misuse of the motivation fund, the management of the distributor company decided that the bonus payment was made by a representative of the supplier - the organizer of the promotion.
Motivation of merchandisers
The goal of motivating commodity experts was to increase the volume and range of products they purchased. Monthly based on the results of the reporting period to these employees, depending on achieved indicators one prize was awarded, which could be chosen among gifts presented in four categories ( household appliances) according to the diagram shown in Fig. 4.

Rice. 4. Motivation scheme for merchandising specialists
Purchase of 10 or more assortment items with a total volume of at least 150 items per month Purchase of 12 or more assortment items with a total volume of at least 250 items per month Purchase of 15 or more assortment items with a total volume of at least 350 items per month Purchase of 18 -ty or more assortment items with a volume of at least 500 pieces per month.
Bright colorful leaflets were produced indicating the terms of the promotion and images of prizes. These promotional materials sales representatives distributors were handed over to merchandisers in retail stores.
Retailer loyalty program
To motivate sellers, the Mystery Shopping method was used. At the same time, at the end of the reporting period, the salesperson of the outlet was awarded a bonus if this employee was recommended by a representative of the target product. Within the framework of the program, five prize places were identified, the total prize fund was 35 thousand rubles in each reporting period.
There was also incentives for efficient display of products, because... Most retail outlets did not have full-time merchandisers, and their functions were performed by salespeople. The prize fund in this case amounted to 35 thousand rubles.
Results of the program implementation
As a result of the campaign, 1,325 retail outlets were covered (there are 3,700 stores in the city in total). The level of product representation was 36% in non-chain retail. During the program period, 320 thousand units of products were sold (5 million 450 thousand rubles in monetary terms). The final sales figures of distributor companies are presented in table. 2.
Table 2. Results of the promotion campaign

The campaign budget amounted to 465 thousand rubles, excluding funds for the implementation of consumer promotions and the ATL campaign. Over the next year, distributors continued shipments to 75% of the retail outlets participating in the promotion. The award ceremony for the winners was organized in the format corporate holiday with the involvement of local media, which became an informational occasion for covering the event in the regional press.
Conclusion
As we can see, conducting an effective trade marketing campaign requires significant organizational and time resources. Given in the article practical recommendations allow you to implement an event with maximum efficiency with a minimum of effort spent on it due to the systematic organization of the project.
Look at the latest receipt from the supermarket. Groceries, washing powder, shower gel - all these products are designated by the short abbreviation FCMG. The decoding of these four English letters speaks for itself - translated into Russian Fast Moving Consumer Goods sounds like “everyday goods” or consumer goods.
Distinctive features of such products:
- Fast turnover – goods are quickly taken off the shelves and replaced with new ones. High turnover brings high profits.
- Short life cycle, due to which consumers have to go shopping almost daily.
- Spontaneous shopping. People are so used to buying these products that they don’t even think twice about adding them to their shopping cart.
- Low price. It reduces the criticality of perception and reduces the decision-making time to a few seconds. The buyer comes to the store and in half an hour or an hour adds 5-10-15 product items to the cart, without seeking advice from the sellers.
Let's figure out what these products are and how to sell them.
FMCG sales categories
There are tens of thousands of product items on the FMCG market. To products wide demand relate:
- food and drinks
- decorative and hygienic cosmetics
- personal hygiene items
- laundry and cleaning products
- pharmaceutical products
- other non-durable goods
- Everyday goods. This group includes perishable food products.
- Products purchased with a reserve. They are characterized by a long shelf life.
- Items needed for receiving guests: decorative paper napkins, disposable tableware, cocktail straws.
Seasonal products are included in a separate category. For example, soft drinks, ice cream and drinking water, the demand for which rises sharply with the onset of the warm season. Or notebooks and pens, sold in large volumes before September 1st.
FMCG market structure
The FMCG market is a highly competitive multi-level environment.
Level 1
At this level, those who come up with and implement new ideas in the field of production of consumer goods work. They are also responsible for developing a common advertising strategy for a branded product, so their margins are maximized.
The question of what fmcg companies are is best answered by their names:
- Mars produces the well-known Snickers and Twix chocolate bars, UncleBens sauces, and animal food.
- Nestlé – candies, coffee, ice cream, breakfast cereals, baby food
- Procter & Gamble – detergents, shaving and personal care products
- Johnson&Johnson – medicines and cosmetics
- Philip Morris International – tobacco products
In addition to manufacturers (who are also most often owners of trademarks), importers are at the first level of the market.
Level 2
Large consignments of goods from manufacturers are distributed across wholesale buyers, which constitute the second level of the FMCG market. However, there are manufacturers who sell directly to end customers. A striking example is Avon.
A distributor or a regular wholesale warehouse company acts as a wholesaler. The latter, unlike the distributor, does not develop client base, does not develop or organize marketing activities, does not cooperate with the manufacturer to promote the product.
The standard markup for a wholesale company is 15-20%, less often up to 40%.
Level 3
Retail stores - chain or individual - closely interact directly with the end consumer.
- Network retail outlets have the same name, uniform design trading floors, similar assortment assortment matrix and general pricing policy with markups of 5-100%
- Single stores work every man for himself. Due to the small volumes of supplies, purchase prices for them are relatively high, which does not allow stores to set a markup above 30%.
The third level in the structure of the FMCG market also includes HoReCa enterprises: hotels, restaurants, catering agencies. The markup on goods reaches 500%.
Level 4
Now we have reached the ultimate goal of any manufacturer - the final buyer. In the FMCG sales segment it is individual purchasing products for their own consumption. This is what they focus on when developing promotion strategies, creating new products, and improving their quality.
Features of the FMCG sales segment
One short sketch will help you understand what FMCG sales is. Imagine you are walking down the street and you are thirsty. You won’t explore the offerings of different stores, but go to the first one you come across and buy a bottle of drinking water with a familiar name on the package, ignoring a dozen others. That's it, the act of sale/purchase is completed, the manufacturer's task is completed.
The example clearly shows the features of sales in the FMCG segment:
- the habit of buying familiar goods quickly, without thinking
- spontaneity of decision-making based on immediate desires
- seasonality (not for all products)
- formation of a specific consumption model
- high level of demand and high competition
- easy replaceability and low cost of goods
All this together contributes to the dynamic development of the market and active competition. To succeed in FMCG sales, you need to carefully consider marketing and regularly conduct advertising campaigns and organize competent merchandising.
You cannot survive in the FMCG market without the help of professionals who will do a huge amount of work:
- They will increase product recognition and flood retail outlets with it
- They will place products in the “golden” areas of the store and arrange them correctly on the shelves
- They will ensure quick turnover, especially for goods with a limited shelf life.
- They will reduce receivables arising from the traditional postpaid system of mutual settlements between the distributor and retailer.
- They will select qualified personnel and motivate them to achieve results.
Recruitment for an FMCG company
The main task of an FMCG business is not just to retain already loyal customers, but also to constantly attract new ones to continuously increase income, which is impossible without the participation of competent and responsible personnel.
Requirements for employees of FMCG companies:
- activity, ability to quickly make independent non-standard decisions
- effective communication skills
- focus on results
- teamwork orientation
- self-motivation and responsibility for one's role
- high leadership potential
Recruiting personnel for an FMCG company is a multi-stage complex process, and during the interview the HR specialist pays attention not to education, but to the personal qualities of the candidate. To identify them, testing is used, based on the results of which the candidate’s compliance with the needs of a particular FMCG business is determined.
As a result of the test, the employer receives an objective assessment of the potential employee based on:
- character type and communication style
- logical and rational thinking
- analytical and communication skills
Marketing tools for FMCG sales
An FMCG company marketer works in several areas at once:
- finding ways to increase trade turnover
- assessment of the level of consumer loyalty
- working out all stages of promotion
- creating an unconscious need among consumers to buy a specific product
- capturing the most advantageous places on store shelves
What marketing tools does he use?
- Research on consumer behavior: where, when, why and why the consumer buys a product.
- Advertising to increase brand awareness.
- Presentation of the product in the maximum possible number of retail outlets.
- Merchandising – display of goods in priority places, expanded display, shelf branding.
- Packaging design that attracts attention and makes you want to buy.
- Promotions: prize draws, tastings, discounts.
It is very difficult to work in all areas of FMCG marketing at the same time. But it’s easy to miss something important, something that can cause a well-thought-out strategy to go to hell. That is why many companies attract outside consultants - a specialist with a fresh, uncluttered view quickly finds weak points and offers extraordinary solutions to bring the product to a leading position.
FMCG market trends
Rotation of product brands, expansion of assortment, revolutionary marketing solutions - this is what the FMCG sales sector means in the next two years. The market is aimed at reducing the shelf life of products, which leads to an increase in turnover.
Experts say that by 2018:
- the number of formats will increase retail chains(including within the same network)
- the share of supermarkets in the total number of FMCG stores will decrease
- the number of retail outlets within walking distance will increase
- the share of FMCG goods from Russian brands will increase
- the number of discounters will increase to 35% (retail stores operating in the low price segment)
- State regulation of the FMCG market will be strengthened
- retail turnover will increase by 3.5-4%
Industry growth is gradually slowing down and competition is becoming tougher. Manufacturers fight tooth and nail for every percentage share of sales. Today you cannot take your place in the FMCG market and rest on your laurels. Need permanent work different directions to maintain and grow the company's position

* The calculations use average data for Russia
INTRODUCTION
The FMCG goods market is one of the most striking indicators of the economic situation in the country. It reflects not only consumer sentiment and confidence, but also the level of solvency, since most FMCG products are essential goods.
According to the definition, FMCG (fast moving consumer goods) are goods of everyday consumption by a wide range of buyers, which have a relatively low cost and high turnover. In other words, these are consumer goods:
Personal hygiene items
Cosmetics
Teeth cleaning and shaving products
Detergents
Light bulbs, batteries and other non-durable goods
Food (sometimes considered as separate category, but more often as FMCG)
A distinctive feature is the low profitability of this type of goods, however, due to large sales volumes and rapid turnover, they represent an economically profitable category.
MARKET ANALYSIS
The market for food and non-food FMCG products has shown a stable trend of falling turnover since the second half of 2014. The reasons for this are the decrease real income population, Western sanctions, weakening of the national currency and other negative factors.
For the entire period from 2014 to 2016, there was only one surge of activity in the market, when the population actively tried to invest cash as much as possible cash. However, the real growth rate of retail trade in 2014 was 2.5%, while in 2013 this figure was at 3.9%. The decline in sales volumes forced players to reconsider their work models and significantly change assortment policy and logistics. With a decrease in turnover in physical terms, in monetary terms, according to RBC, retailers' turnover increased by 30%. The share of chain retail (food) in the market structure has also increased; in 2014 it amounted to 37.8% (+5.8 percentage points).
In general, the development of chain retail in Russia is uneven. The provision of chain stores per capita lags significantly behind the indicators of developed countries. At the same time, in some cities there is an excess of chain retailers, while in others there is a shortage.
According to analysts, by mid-2015 a number of trends had emerged that will determine further development market until the end of 2017:
Increasing the variety of formats within one retail chain, including through the introduction of discount formats (discounters);
Increasing the share of modern formats in FMCG retail to 60-65% in 2016;
Increasing the share of goods Russian production in assortment (up to 40-50%) and chain revenue, associated with the import substitution policy; development own production;
The growing popularity of discounters (stores with a range of products in the low price segment);
Decrease in consumer activity of the population, reduction in expenses, high degree of influence of price on the purchase decision;
Changing the development strategy and business models of networks to reduce the share of borrowed funds in total capital due to their high cost;
Refusal to open some new stores (however, some discount chains, on the contrary, began to actively develop the format of “convenience stores”;
Growing influence government regulation industry, increasing the tax burden on business.
The dynamics of GDP growth reflects the general state of the entire economic system countries. If at the end of 2011 - beginning of 2012, GDP showed growth of 4-5% per quarter, then in the second quarter of 2015, with a stable preliminary fall, it was already -5%. However, at the beginning of 2016 the decline dropped to -1%.
The prerequisites for the crisis are obvious: EU and US sanctions, the weakening of the ruble, a significant drop in oil prices. As a result of these processes, the cost of imported products has increased significantly. Since the production of many domestic goods uses imported technologies, raw materials, components, equipment, etc., product prices Russian manufacturers also increased. According to Rosstat, prices for goods and services in 2015 increased by an average of 12.9% compared to 2014.

Earn up to
200,000 rub. per month while having fun!
Trend 2019. Intellectual business in the field of entertainment. Minimum investment. No additional deductions or payments. Turnkey training.
Figure 2. Consumer Confidence Index, Q1 2008 – Q1 2016
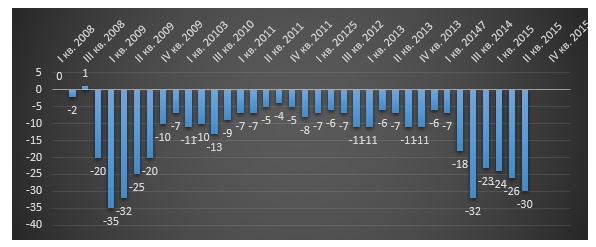
As can be seen from Fig. 2, the consumer confidence index has approached the values of the crisis year 2008, which directly affects the development of retail trade. However, experts, in particular RBC.Quote, predict an improvement in the economic situation in 2017–2018. and an increase in Brent oil prices to $66.4 per barrel. Experts also predict a decrease in inflation rates and growth in consumer prices (up to 4.9%).
However, even against this background, according to the Ministry’s forecasts economic development, real disposable income of Russians in 2016 will decrease by 2.8% due to high debt levels, rising prices, unstable economic and political situation and other factors. This will force the population to take a more balanced approach to spending.
Figure 3. Nominal volume of retail trade in the Russian Federation, billion rubles, 2009-2018 (data from RBC, according to sources from the Ministry of Economic Development and Trade)

In the future, until 2018, experts predict an increase in household incomes and the restoration of the consumer lending system, which will lead to increased consumption. In 2018, according to forecasts, retail trade turnover growth will be 3.7% in volume terms. The savings rate will decrease, which will lead to some increase in spending by the population.
Ready ideas for your business
Retail trade and the services market have traditionally ensured the growth of Russian GDP. However, against the backdrop of the economic recession, these segments began to lose their role as the main factors in economic development.
Figure 4. Share of retail trade in the structure of Russia’s GDP, %, 2004-2014.
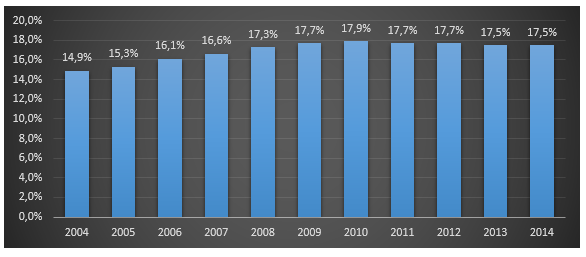
Figure 5. Share of retail trade turnover of retail trade networks in the total volume of retail trade turnover, %

In the non-chain retail trade segment, there has been a decrease in the number of small and micro-enterprises due to increased competition from retail chains, as well as an increase in the tax burden on small businesses and an increase in the cost of loans.
Ready ideas for your business
There have been no significant changes in the structure of retail trade formats in recent years. The discounter format showed some growth, while the supermarket format showed a decline, which will continue to decline in the near future. Large-format retail (hypermarkets) showed high resistance to crisis factors, but its share still decreased slightly. Convenience stores showed an increase. This format is developing today as federal companies, and, traditionally, local players.
Since 2013, experts have noted a significant increase in the share of “other” formats: eco-goods stores, “fix-price” format stores, etc. In 2014, they accounted for at least 10% of the total retail turnover. Presumably, this share will grow.
The number of food manufacturers' own chain stores is also growing: poultry, dairy products, bakery products.
Figure 6. Structure of retail formats (by number of outlets) in Russia
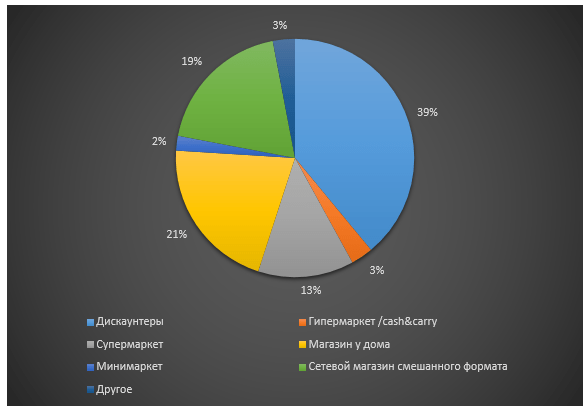
Retail market development forecasts (FMCG segment):
Reducing the share of large-format retail and increasing the share of discounters (within 35%)
Reduction in the share of supermarkets amid declining customer traffic
Development of convenience stores (up to 12-13% of the total)
Emergence of new store formats
Denis Miroshnichenko
(c) - portal of business plans and guides for starting a small business
86 people are studying this business today.
In 30 days, this business was viewed 20,581 times.
Calculator for calculating the profitability of this business

An analysis of the cargo transportation industry, as well as affiliated industries, clearly indicates a decline in the country’s economy as a whole and, as a result, a decline in the results of this market. In addition to external negatives...