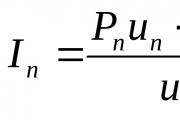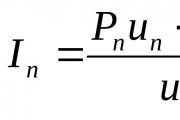26.08.2022
What is included in the salary? Salary concept
How to correctly determine the composition of wages and why is it so important? What is included in the salary? It seems like a simple question with an obvious answer: salary is what the employee receives from the employer. Don't rush to conclusions.
Why do errors occur in salary payments?
Yulia Busygina comments, presenter of the online course Kontur.School ""
:
“Often errors arise due to the fact that the accountant classified “non-salary” compensation payments as wages. For example, an employer reimbursed an employee for expenses for cellular communications or for the use of personal transport. Such compensation is not part of the salary. After all, this is not payment for labor, but simply compensation to the employee for communication expenses. Such amounts cannot be included in average earnings»
Three components of salary
Remuneration for work
|
Compensation payments
|
Incentive payments
|
| The employee will receive what he has “earned.” It depends on his qualifications, complexity, quantity, quality and working conditions |
Additional payments and allowances for work:
- In conditions deviating from normal (for example, working at night)
- In special climatic conditions and in areas exposed to radioactive contamination
- Other compensation payments
|
These include:
- Additional payments and bonuses of an incentive nature
- Awards (we recommend recording a webinar about)
- Other incentive payments
|
What and why cannot be included in the salary
When is a bonus a salary and when is it not?
We have already figured out that bonuses are classified as payments stimulating nature. But oh It is a mistake to believe that any bonus paid to an employee is his wages.
Bonuses can be classified as wages if they are paid for work (labor) that the employee performs in accordance with his job responsibilities. Such bonuses must be reflected in the employment contract with the employee and in the company’s local regulations.
Some types of bonuses, for example for an anniversary date, cannot be classified as salary.Agree, it is absurd to consider money received for an anniversary as salary. And it doesn’t matter that such payments are called “bonuses” in the company’s local regulations and contracts.
Accountant's Memo
- Attribute a bonus to salary if it is paid for work or labor performed in accordance with job duties.
- A bonus that is not a salary cannot be included in labor costs when determining the income tax base.
- Check the composition of wages to avoid errors when calculating average earnings and when determining the taxable base for “salary” taxes.
Posted on 11/21/2017
tariff rate (salary) and an additional part - additional payments, allowances, bonuses.
tariff rates And salaries
surcharges
- for work in areas of radioactive contamination (Article 33 of the Law of the Republic of Belarus “On social protection citizens affected by the disaster Chernobyl nuclear power plant") additional payments are made taking into account the level of radioactive contamination of a particular area and the nature of the work performed within the minimum and maximum limits;
Unlike surcharges, allowances
awards
LITERATURE:
SEE MORE:
TO permanent part These include payments, the frequency of receipt and the amount of which do not depend on the results of the employee’s work. This is a kind of guaranteed part of the salary: salaries, bonuses for length of service, for qualifications. Also, the permanent part of wages can include compensation payments due to working conditions, for example, additional payments for harmfulness, as well as those associated with personnel costs - travel, cellular and etc. Variable part wages, on the contrary, are tied to quantitative and qualitative indicators of labor. It can be in the form of bonuses or the entire salary, depending on what functional duties the employee performs and what are the criteria for evaluating his activities.
There are various principles for the formation of wages on the following grounds: 1) application of tariff rates; 2) individual or collective distribution of wages on various grounds.
1) Application of tariff rates
Tariff rates- this is the absolute amount of wages expressed in monetary terms per unit of working time or per unit of production.
There are two forms of tariff payment system: piecework and time-based. In the piecework form, payment is made for the quantity of products made. The basis of calculation is the piece rate, which expresses the cost of manufacturing a unit of production or product. With a time-based form, you are paid for the time worked. Here the basis of calculation is tariff rates, i.e. the cost of an hour, day, week or month of work.
Piecework form of remuneration Direct piecework- applicable to key personnel of companies producing goods and services, if the result can be measured quantitatively. In cases where personnel are also rewarded for exceeding the plan and for meeting quality labor indicators, for example, the absence of a barque, saving resources, then the payment system will have the name piecework-bonus. And when piecework-progressive system, bonuses for exceeding the plan are accrued at progressively increasing rates. Indirect piecework the payment system is used, as a rule, for auxiliary workers production organizations. The earnings of auxiliary workers depend on the output of the main production workers they serve. Chord- the total amount of earnings of the group (crew) is agreed upon before the start of work according to current standards and piece rates. The work must be completed on time. What does the salary consist of?
Failure to meet deadlines and quality of work entails penalties in the form of deduction of “penalties” from the total amount of earnings. This payment system is applicable to all project teams. If bonuses are also provided, then the system will chord-premium The essence commission system wages is that wages are determined as a percentage of sales. It is applicable for sales workers. Time-based form of remuneration Simple time wages- payment for actual time worked at the tariff rates of an employee of this category. Hourly, daily, and monthly tariff rates can be set. In case of menstruation tariff rate the system is called salary. If a bonus is also provided, then the system will time-bonus. The time-based form of remuneration is used in cases where it is difficult to quantify the result of labor.
|
The tariff system involves rationing of labor. The standards serve as the calculation base for wages and are used in calculating bonuses and in assessing performance. There are production standards, time standards, wage standards, labor intensity standards, and service standards.
Non-tariff systems differ from tariff systems in that prices and tariffs are not used when calculating wages.
Salaries are formed according to other principles, for example, the amount of wages is set by agreement with the employee, a pre-agreed overall result is paid, etc. In general, the tariff-free payment system provides the payment system developer with a lot of scope for “flights of fancy.”
2) Individual or collective distribution of wages
Individual distribution involves determining wages based on the employee’s personal merits, past or present. Moreover, the assessment of individual merits and determination of the amount of payment can take place both in the form of an objective assessment of the employee’s work results, and in the form of a subjective assessment of the manager or group. In addition, certification can be used to determine individual merits: based on the results of certification, the employee is assigned an appropriate coefficient of professionalism or qualifications, which subsequently determines the level of his salary.
When collectively distributing wages, the principle of sharing a limited amount is used, taking into account the contribution of each group member to general work. The magnitude of the share contribution is characterized by KTU (coefficient labor participation)
, which, like the individual merits of employees, can be determined in different ways: from a subjective assessment of a manager or group to calculations using complex formulas. KTU can also be determined on the basis of standards developed at the enterprise, including the basic level of KTU and indicators, if met or not met, the KTU increases or decreases.
It should be noted that it is necessary to distinguish between the concepts of constant and variable parts of wages and the concepts of basic and additional wages.
Basic salary- payment for work performed. Additional payments- this is what is paid in addition to the basic salary: bonuses, bonuses, compensation payments. Both the basic salary and additional payments may consist of fixed and variable parts. So, for example, with a piecework form of payment, the amount of wages will vary depending on output, i.e. main part- variable. In this case, the employee can receive as additional payments bonus for length of service - a constant payment that does not depend on the results of work, as well as compensation for harmfulness, also a constant payment.
It is generally accepted that for most positions the size of the permanent part should be in the range of 30 to 70 percent of the total salary. The bottom line is that the volume of the permanent part should be approximately equal to the employee’s subsistence level, the constant part of the salary should not be enough, it should provoke the employee to strive to earn more by increasing the volume of variable payments. And despite the fact that the variable part of the salary is always tied to the employee’s performance, its increase is beneficial for the company too.
The role of the payment system in solving company difficulties
Adjusting the remuneration system can help a company cope with the following problems:
- staff turnover and difficulties in recruiting staff;
- low productivity and inefficiency;
- poor quality of staff work;
- customer departure and ineffectiveness of the customer base;
- low professional level of some employees and irreplaceability of others.
Date of publication: 2015-02-03; Read: 1135 | Page copyright infringement
studopedia.org - Studopedia.Org - 2014-2018 (0.002 s)…
SALARY STRUCTURE
The salary consists of two parts: the main part - tariff rate (salary) and an additional part - additional payments, allowances, bonuses.
When establishing the size of menstruation (hourly) tariff rates And salaries employers should proceed from the fact that rates and salaries should ensure wage differentiation depending on the level of qualifications of workers, the complexity and responsibility of the work they perform. Taking into account other factors of its differentiation in wages - conditions, labor intensity, the importance of areas of its application, quantitative and qualitative results of labor - is carried out with the help of other elements of remuneration - allowances, additional pay, bonuses. The tariff rate (salary) of a particular employee serves as a calculated value for determining the amount of allowances, additional payments, bonuses and other payments due to him. Although some additional payments, due to their objective nature, for example, for work at night, in unfavorable working conditions, are calculated as a percentage of the monthly minimum wage or the tariff rate of the first category.
The above-tariff part of wages consists of allowances and surcharges, the difference between which is that the former are mainly stimulating, and the latter are of a compensating nature.
The legislation provides certain types additional payments and allowances that are mandatory for all employers. These primarily include surcharges for working in working conditions different from normal:
- for work in a multi-shift (two- and three-shift) mode, for work at night - not lower than those provided for in Art. 70 TK RB sizes;
- for intensive work, in particular for combining professions (positions) or performing the duties of a temporarily absent employee (Article 67 of the Labor Code of the Republic of Belarus), the amount of additional payments for extra-budgetary sphere are established by the employer by agreement with the employee, and for organizations financed from the budget - by the Government of the Republic of Belarus;
- for work in difficult and harmful production conditions (Article 62 of the Labor Code of the Republic of Belarus) - based on data from certification of workplaces and instrumental measurements, a list of works and workplaces with deviations from regulatory conditions. Then specific amounts of additional payments are established and this data is included in the collective agreement. Every year, as manual labor becomes mechanized and its conditions improve, the list is updated;
- for work in areas of radioactive contamination (Art.
What does the salary consist of?
33 of the Law of the Republic of Belarus “On the social protection of citizens affected by the disaster at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant”), additional payments are made taking into account the level of radioactive contamination of a particular zone and the nature of the work performed within the minimum and maximum limits;
- for work in areas with difficult climatic conditions - used mainly for employees of enterprises performing work on a rotational basis.
Unlike surcharges, allowances, as a rule, are installed at the discretion of the employer. The legislation knows the following types of allowances: for qualification classes; for high professional excellence; for high creative, production achievements in work or for performing particularly important (urgent) work; for work experience in certain industries (science, education, culture, etc.); for knowledge and application of foreign languages in everyday work; behind academic degrees; for mobile and traveling character work; performing work on a rotational basis; for constant work on the road; work outside permanent place residence, etc.
Along with bonuses, the stimulating element of wages is awards. Bonuses are in the nature of periodic (monthly, quarterly) payments for the results of individual or collective work. For work overtime, on public holidays, public holidays and weekends, bonuses are calculated on earnings at single piece rates or at a single tariff rate, salary.
Indicators, conditions, sizes, sources of bonus payments everywhere, including in budgetary sphere, are determined by the provisions on bonuses, which serve as an annex to the collective agreement or as independent local acts, approved by the manager.
Bonuses as an element of wages should be distinguished from bonuses as incentive measures (Article 196 of the Labor Code of the Republic of Belarus). Under the bonus wage system, an employee can claim a bonus in a claim if he has fulfilled the indicators and conditions of the bonus, but cannot claim an incentive, one-time bonus.
The question of the salary structure, i.e. on payments related to wages has important practical significance, in particular, for taxation, indexation, calculation of state social insurance contributions, calculation of average earnings, etc.
LITERATURE:
1. Commentary on the Labor Code of the Republic of Belarus / Under general. ed. G.A. Vasilevich. – Mn.: Amalthea, 2000, R. II, Ch. 6, p. 260-328.
2. Labor law: Textbook / V.N. Artemova, G.A. Vasilevich and others; Under general ed. Semenkova V.I. – Mn.: Amalthea, 1997, Ch. 7, p. 208-211.
Previous891011121314151617181920212223Next
SEE MORE:
 Surely, every employee would like his wages to meet his needs, wages that would allow him to provide his family with everything necessary. When setting wages, the employer takes into account production costs, the prevailing level of wages in the industry, and also expects to make a profit.
Surely, every employee would like his wages to meet his needs, wages that would allow him to provide his family with everything necessary. When setting wages, the employer takes into account production costs, the prevailing level of wages in the industry, and also expects to make a profit.
Therefore, the interests of the employer and employee regarding the sphere of remuneration come into conflict? What is salary? How are wages calculated? Not every employee fully understands the meaning of such concepts. We invite you to look into these issues together.
Salary or wages
The concepts of “salary” and “remuneration” are completely equivalent. In the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, both of these meanings are used, without actually making any differences between them, guided only by the principle of euphony in certain expressions.
Initially, labor legislation distinguished between the following concepts: remuneration as a system of labor relations, and wages as material remuneration. However, in the current edition of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, such a difference has been eliminated.
By definition, wages (wages) are material (monetary) remuneration for work, depending on the qualifications of the employee, the volume, quality and complexity of the work, including incentive payments, as well as guarantees and compensation to employees for work in difficult conditions. The concepts of “wage” and “wages” are closely related to the concept of minimum wage (minimum wage).
Payroll
Any accruals, be it wages, vacation pay, bonuses and other payments, are made on the basis of local regulations. Salaries are calculated according to salaries, tariff rates, taking into account additional payments for deviations in working conditions, night work, overtime, piecework rates, payment for forced downtime due to the fault of the employer, and the like.
Additional payment is payment for unworked time, namely: additional breaks for nursing mothers, performance of public duties, vacations, as well as benefits associated with dismissal and disability.
The remuneration of each employee must be recorded in the employer’s orders.
Procedure and terms of payment
The employer notifies each of his employees in writing about the payment of wages, including the amount of wages accrued to him, its components, the amount of deductions and the amount to be received. Payment of wages is carried out either at the place of work or by transfer Money to the employee's bank card. Payment conditions are established by a collective or individual employment contract.
Payments are made at least twice a month directly to the employee. If the day specified for payment falls on a weekend or holiday, payment is made on the previous working day.
Form of remuneration
There are several forms of remuneration: piecework and time-based.
Piecework is a wage in which payment is calculated from the number of units of product produced in a certain period, taking into account the quality of the product and the complexity of working conditions.
Types of piecework wages include:
- direct piecework - wages directly dependent on the number of products produced, work performed, based on fixed prices taking into account the qualifications of the employee;
- piecework-bonus – provides for the accrual of bonuses for exceeding production standards;
- piecework-progressive - payment for manufactured products within the norms at established prices, and products exceeding the norm are paid at prices according to a progressive scale, but not higher than double the rate;
- chordal – provides for an assessment of the volume of various works indicating a specific deadline for their completion;
- indirect piecework - used to improve labor productivity in servicing equipment and workplaces. The work is paid based on the product produced by the main worker.
Time-based is a form of payment in which the salary depends on the time worked, taking into account the working conditions and qualifications of the employee.
With this form of payment, the employee is assigned time-standardized tasks. There are different simple time views payments and time-based bonuses:
- simple time-based – payment for time worked, regardless of the size of the work performed;
- time-based - bonus - payment for time worked at a rate with bonuses for the quality of work performed.
To ensure the material interest of employees in fulfilling plans, bonus systems are used: remuneration (bonus) based on work results and other forms of material incentives.
Violation of deadlines for payment of wages and salaries
In case of failure to pay wages on time, the employer is subject to liability in accordance with federal law.
If the period of delay in payment is more than 15 days, the employee has the right to stop work until the debt is paid, but must notify the employer. It is not allowed to stop work during a period of martial law or a state of emergency, in military and paramilitary formations, by civil servants, workers whose labor function is related to ensuring the livelihoods of the population, as well as those serving hazardous industries.
During a work stoppage, the employee has the right not to be at the workplace and is obliged to return to established regime working hours no later than the next day after receiving notification of the employer’s readiness to pay wages.
For each day of delay, the employer is obliged to pay monetary compensation and compensate for moral damage caused to the employee.
Employees have the right to protect their rights to receive wages by filing the following claims in court:
Claim for recovery of wages
Statement of claim for recovery monetary compensation for delay in payments
Statement of claim for wage indexation
Statement of claim for recovery of severance pay
Statement of claim for moral damages from the employer
The concept of remuneration also includes various types of compensation charges (for example, heavy working conditions), as well as additional payments and bonuses, which are payments that motivate work. Thus, the wage structure at the enterprise consists of three parts:
- Main.
- Various compensations and allowances.
- Employee incentive payments.
The basic part is determined based on the type of payment system for the work performed. The main condition is that its size cannot be less than the minimum wage. Thus, the basis of the salary is precisely the basic part. Its size may be influenced quantitative expression sales, income received by the organization, and many other nuances.
What is included in the salary structure?
The remuneration of these workers is made as a percentage of the rates of the main categories of workers. The time-based remuneration system links payment with the quantity and quality of work by establishing the dependence of remuneration on the time spent on performing labor function and on the qualifications of the employee. In a time-based system, wages are calculated based on the employee’s tariff rate (salary) and the actual time worked.
Attention
The bonus system, which complements the piecework and time-based systems, makes it possible to materially reward the achievement of better labor results. Bonuses are awarded to employees based on the regulations in force at enterprises, institutions, and organizations.
9. salary
Many organizations and enterprises prefer to hire young and socially active people, energetic and active.
- National and cultural characteristics also affect wages. The wage structure at each enterprise is different, so this factor can be taken into account.
- Territorial and geographical characteristics.
In regions where a harsh climate prevails and, accordingly, more difficult working conditions, wages are often significantly higher. In addition, workers in harsh conditions can count on receiving various types of benefits.
These include receiving extended vacation (up to 2-3 months) and the possibility of free travel around the country.
- The level of general economic development of the country, as well as the overall development of the labor market.
There are two main forms of payment for work: piecework and time-based.
What does the salary consist of?
If you want to find out how to solve your particular problem, contact us through the online consultant on the right or call free consultation: Structure according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation Some changes have occurred in the legislation (No. 90-FZ), in particular in Article 129 Labor Code Russian Federation, and wages for this moment is synonymous with wages. Wages (employee remuneration) are remuneration for work, which depends on its qualifications, quality and complexity.
Compensation charges are also included in the concept of wages, including for work in difficult conditions, as well as payments motivating work (additional payments and bonuses). This structure consists of the following parts (see.
What components does salary consist of?
- basic (main) part;
- compensation payments;
- incentive payments.
The base part is determined from the basic payment system for the work.
Info
Read also the article ⇒“Salary for an incomplete month in 2018” Is the employer obliged to provide a payslip? The employer’s obligation to notify the employee about wages is regulated by Art. 136 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The payslip must contain the following information:
- components of wages due to the employee for the relevant period;
- the amount of other amounts accrued to the employee, including monetary compensation for the employer’s violation of the established deadline for payment of wages, vacation pay, dismissal payments and (or) other payments due to the employee;
- the amount and reasons for the deductions made;
- the total amount of money to be paid.
The purpose of issuing a pay slip is to inform the employee what his next salary consists of.
Composition and structure of employee wages
OKPDTR consists of two sections:
- workers' professions;
- employee positions.
The first section - professions of workers - includes professions of workers in accordance with the Unified Tariff and Qualification Directory of Work and Professions of Workers (UTKS), as well as professions of workers whose rights and responsibilities are provided for in charters, special provisions and relevant regulations regulating the composition of professions in sectors of the economy .
The second section - employee positions - was developed on the basis of the Unified Nomenclature of Employee Positions, Qualification directory positions of managers, specialists and employees, current regulations and other regulatory documents on remuneration issues, taking into account the titles of positions used in the economy.
Topic 2.3. wages according to labor law
Of course, such actions do not occur in accordance with the law. Regulations for calculating average monthly wages are prescribed in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (Article 139).
Therefore, when an employer calculates the average monthly salary, he needs to take into account:
- accrued actual payments for the last year;
- hours worked in each month.
A month is its duration according to the calendar (from the first to the thirty-first day, except February).
Components of wages
It is based on piece rates and labor standards in the form of production standards or time standards. The production rate establishes how many products of appropriate quality a worker must produce per unit of time (per hour, day).
The standard time indicates how much time a worker is given to produce a unit of product or perform a production operation. A piece rate is the rate of remuneration for a unit of product manufactured by an employee or an operation performed by him, taking into account the complexity, that is, the level of qualification (category) of the work performed. Piece rates are determined by dividing the hourly (daily) tariff rate corresponding to the category of work performed by the hourly (daily) production rate.
Salary at work
The advantage of a piece-rate wage system is that the employer does not need to control how employees use working time, since each employee is interested in producing more output. But piece-work payment labor cannot be applied everywhere.
To use it, you need to have a real opportunity to record quantitative indicators of labor results. If, with piecework wages due to objective circumstances beyond the employee’s control, the quantity of products produced, services provided or goods sold does not allow the employee to receive a salary of at least the minimum wage, then, since the employee has worked the full standard working time for the month, he cannot be paid wages paid below the minimum wage.
Example of piecework wages: The organization has established direct piecework wages.
Chapter ix. wage
It is important to understand that wages do not include some benefits provided to the employee. This article will be devoted to this issue.
What does the salary consist of? According to Art. 129 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, wages (employee remuneration) consists of:
- remuneration for labor depending on the qualifications of the employee, complexity, quantity, quality and conditions of the work performed (salary);
- compensation payments (additional payments and bonuses of a compensatory nature, including for work in conditions deviating from normal, work in special climatic conditions and in territories exposed to radioactive contamination, and other payments of a compensatory nature);
- incentive payments (additional payments and incentive allowances, bonuses and other incentive payments).
Dedicated to the rules for paying wages to employees. In particular, cases are listed when the employer has the right to reduce the employee’s wages. It is also explained which payments are included in the salary and which are not.
Salary composition
Rostrud specialists remind that the salary includes the following parts:
- Salary (official salary), tariff rate;
- Compensations, namely additional payments and allowances for work in special climatic conditions; remuneration for work in conditions deviating from normal (that is, for work in harmful or dangerous working conditions; for work at night; for combining positions, etc.);
- Incentive payments (for example, additional payment for length of service; bonuses for performing specific work, based on the results of the reporting period, for quitting smoking, for saving consumable materials, etc.).
Vacation pay is not included in salary
At the same time, the salary does not include compensation payments listed in the article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. These are, in particular, the amounts that are paid when sent to business trip; when moving to work in another area; in case of forced cessation of work through no fault of the employee; when providing annual paid leave; due to a delay due to the fault of the employer in issuing work book upon dismissal of an employee.
Salary slip
Salary cannot be lower than the minimum wage
Please note: unlike other payments, the regional coefficient and percentage bonus for work experience in the Far North and equivalent areas are not included in the minimum wage.
Wage indexation
Also, Rostrud specialists remind that the employer is obliged to index wages in connection with the increase in consumer prices for goods and services (Article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The procedure for indexing wages is determined in a collective agreement, agreement, or local regulation. If according to the results calendar year, during which Rosstat recorded an increase in consumer prices, wages are not indexed, the employer may be held liable, regardless of whether the corresponding local act or not.
When can an employer reduce wages?
By general rule, changing the terms of the employment contract, including in terms of reducing wages, is allowed only by agreement of the parties to the employment contract. But in some situations, a monthly salary may be paid in a smaller amount than established in the employment contract, without the consent of the employee. Such cases include:
Based on the definition of wages given in Article 129 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, its components can be identified. The salary structure consists of the following parts:
1. the main (constant) part of the salary;
2. compensation payments;
3. incentive payments.
Main part of salary is established on the basis of the current employer’s remuneration system and cannot be less than the established federal law Minimum wage. The main part of the salary is its constant component; it does not depend on the profit received, sales volume and other indicators. The main part of the salary is accrued for the time actually worked or the work actually performed at tariff rates and official salaries.
When setting the basic part of the salary, the employer must be guided by the following principles:
— the salary of each employee should depend on his qualifications, the complexity of the work performed, the quantity and quality of labor expended;
— any kind of discrimination in establishing and changing wage conditions is prohibited;
— for work of equal value, the employer is obliged to provide equal pay to employees.
Compensation and incentives payments are a variable part of wages, which depends on the guarantees established by the state and the conditions of remuneration established by a given employer.
Compensation and incentive payments are not related to payment for time actually worked or work actually performed.
For this part of wages, the method of local regulation is more inherent, especially for incentive payments, when the basic rules for their establishment are determined by law.
A number of compensation payments are established by law, their payment is the responsibility of the employer:
a) for performing work under special conditions (work in heavy work, work with harmful and (or) dangerous and other special working conditions, work in areas with special climatic conditions);
b) for work in areas exposed to radioactive contamination;
c) for performing work in conditions deviating from normal (performing work of various qualifications, work when combining professions (positions), expanding service areas, increasing the volume of work or performing the duties of a temporarily absent employee without release from work specified in the employment contract, overtime work, working at night, on weekends and non-working holidays and performing work in other conditions deviating from normal);
The specific amounts of compensation payments are determined by the collective agreement, agreements, local regulations, an employment contract and cannot be lower than the established labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms.
In addition, the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides for increased wages for persons working on a rotational basis and for persons working in the Far North and equivalent areas by introducing the following payments into the wages:
— persons working on a rotational basis are provided with an allowance for the rotational method of work: “for each calendar day of stay in places of work during the shift period, as well as for the actual days of travel from the location of the employer (collection point) to the place of work and back ";
— persons working in the regions of the Far North and equivalent areas are paid using regional coefficients and percentage increases in wages.
Thus, the main purpose of compensation payments is to reimburse the employee’s additional labor costs, which are associated with the work schedule, working conditions, characteristics labor activity and character individual species labor. They are calculated in addition to official salaries and tariff rates.
Incentive payments(additional payments and allowances of an incentive nature, bonuses and other incentive payments) - this is a variable part of the salary, which may depend on the profit received, on the employee’s individual contribution to the result economic activity and so on.
Bonuses and other incentive payments, unlike most compensation payments, are not regulated at the legislative level; their payment is the right of the employer. But it should be noted that if bonuses and other incentive payments are provided for by the remuneration system, then the employer has an obligation to pay them, and the employee, if he fulfills the indicators and conditions of the bonus, has the right to demand payment of these incentive payments.
Thus, incentive payments as part of wages can be characterized as cash payments for achieving certain results in work.
The main purpose of using additional payment systems, incentive allowances and bonus systems is aimed at creating a material interest among employees in achieving those indicators that are not provided for by the basic payment at tariff rates and salaries, as well as stimulating employees to increase professional level, reducing staff turnover, attracting the necessary highly qualified specialists.
Incentive payments (additional payments or allowances) can be established:
- for high qualifications;
— work experience in the organization;
- knowledge of foreign languages, etc.
To stimulate employee interest in improving the quality of work in organizations, a bonus system is used. Payment of bonuses is an incentive for conscientious performance labor responsibilities. Awards can be divided into two groups:
a) Bonuses included in the remuneration system.
The employee’s right to receive this bonus, and accordingly the employer’s obligation to pay it, arises subject to the achievement of specific indicators predetermined by the bonus system. Otherwise, the right to a bonus does not arise.
b) Prizes, not provided by the system wages.
These bonuses are in the nature of a one-time incentive at the unilateral discretion of the employer and are paid, as a rule, irregularly, in addition, they are not related to specific achievements in work. In this case, incentive bonuses are a right and not an obligation of the employer, therefore its conditions are determined by the employer independently and do not require a pre-formalized basis.
Bonus indicators must correspond to the types and tasks of production, reflect the connection with the labor contribution of each employee and the team as a whole. The number of indicators and bonus conditions should not exceed two or three, otherwise the connection between the bonus system and the main production tasks may be lost. Indicators should not contradict each other - improvement of some should not contribute to the deterioration of others.
Indicators and conditions of bonuses workers, their initial levels are determined in accordance with the planned performance indicators of the site, workshop, taking into account the degree of influence of workers on their change.
When stimulated product quality
. works and services use the following indicators:
· improving product quality,
· no complaints about the product.
In order to stimulate the reduction of material costs set bonus indicators:
· for saving raw materials, materials,
· fuel and energy resources, tools, spare parts,
· reduction of waste per unit of production.
Bonus indicator achievement level can be set based on achievements in the base period or higher. Premium amount it is necessary to differentiate, taking into account the intensity of the established bonus indicators, by introducing different scales with a proportional or progressive increase in the size of bonuses depending on the degree of improvement in indicators compared to the base level.
Bonus frequency(month, quarter, year) must take into account the peculiarities of the organization of production, the nature of the product, and the duration of the production cycle.
To operate effectively, the company’s management must take appropriate actions to encourage employees to be interested in their work. Work motivation is one of the most important functions of personnel management.
Work motivation— a set of driving forces for growth productive force labor.
These driving forces include not only material benefits, but also moral ones, expressed in satisfaction with work, in the prestige of work, in the fulfillment of internal human attitudes and moral needs.
The main forms of stimulating the work of employees at the enterprise are:
- material incentives, including wages, bonuses, additional wages, discounts for services, provision additional rights, benefits, etc.;
- financial punishment reduction, deprivation of bonuses, reduction of wages, fines, partial, full or increased compensation for damage caused to the enterprise, etc.;
- moral encouragement workers by expressing gratitude, awarding insignia, promotion to new, prestigious positions at work, including in informal groups outside of work (circles, creative, public associations), provision of additional rights (free working hours), involvement in enterprise management, etc.;
- moral punishment for omissions and shortcomings in work by issuing a reprimand, reprimand, deprivation of benefits and advantages, removal from prestigious positions, deprivation of honorary titles and the extreme measure of dismissal from work.
Wages are the main source of incentives and income for employees of an enterprise. Therefore, its size is regulated by the state and enterprise managers.
Wage- this is part of the social product, which is given to the worker in cash in accordance with the quantity and quality of the money spent.
Basic salary- remuneration for work performed in accordance with established labor standards (tariff rates, salaries, piece rates).
Additional salary- remuneration for work in excess of the established norm, for labor successes and for special working conditions (compensation payments).
Organization of remuneration
The organization of remuneration is understood as a set of measures aimed at remuneration for work depending on its quantity and quality. When organizing work, the following activities related to labor rationing, tariff regulation of wages, development of forms and systems of remuneration and bonuses for workers. Labor rationing is based on establishing certain proportions in labor costs required to produce a unit of product or to perform a given amount of work in certain organizational and technical conditions. The main task of labor regulation is the development and application of progressive norms and standards.
The main elements of tariff regulation of wages: tariff rates, tariff schedules, tariff and qualification reference book.
Tariff rate- the absolute amount of wages expressed in monetary form per unit of working time (there are hourly, daily, monthly).
Tariff schedule- a scale consisting of tariff categories and tariff coefficients, which allow you to determine the salary of any employee. Different industries have different scales.
Tariff and qualification guide- a normative document, according to which everyone tariff category certain qualification requirements, i.e. all main types of work and professions are listed and necessary knowledge to carry them out.
Elements of wages
Currently, the main elements of remuneration are salary schemes and types of wages. The minimum wage (formulation of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation) is social norm and represents the lower limit of the cost of unskilled work force, based on 1 month.
Salaries of engineers and employees determined by staffing table
, i.e., based on the salary schedule and the number of employees in each group.
Salary fund students determined from the number and benefits which they receive. The wages of workers, piece workers and time workers are calculated separately. Workers' wages determined based on technical standardization, i.e., based on the development of standards for labor time spent per unit of production. Labor cost standards include time standards, production standards, and service standards. Production rate is a task for a pieceworker to produce products of the required quality per unit of time under certain conditions. Standard time is a period of working time (hours, days) during which a worker must produce a certain amount of product. The maintenance rate determines the number of machines that a given worker (or several) must service during a shift.
IN modern conditions labor Relations in companies are built on the basis of employment contracts.
Employment contracts come in the form:
- Labor agreement — legal act regulating social and labor relations between employees and employers; is concluded at the level of the Russian Federation, subject of the Russian Federation, territory, industry and profession. An employment agreement is established between the contractor and the customer, the employee and the employer.
- Collective agreement— a legal act regulating social and labor relations between the organization’s employees and the employer; provides for the rights and obligations of the parties in the field of social and labor relations at the enterprise level.
Real wage- the number of goods and services that can be purchased with a nominal salary.
Real wage = (nominal wage) / ()
The study of wage dynamics is carried out using indices.
The individual wage index can be determined by the formula:
Wages can be paid for both time worked and unworked.
To determine the amount of remuneration, taking into account its complexity and working conditions of various categories of workers great importance has a tariff system.
Tariff system- this is a set of standards, including tariff and qualification reference books, tariff rates, and official salaries.
The tariff and qualification directory contains detailed characteristics of the main types of work, indicating the requirements for the qualifications of the contractor.
Tariff rate- this is the amount of payment for work of a certain complexity produced per unit of time.
There are two main systems of remuneration: piecework and time-based.

Piecework form of remuneration
Piece wage system produced at piece rates in accordance with the quantity of products (work, services) produced. It is divided into:
1. Direct piecework(the employee’s earnings are set at a predetermined rate for each type of service or product produced);
Example: a worker’s hourly rate is 30 rubles. The standard time for producing a unit of product is 2 hours. Price per unit of production is 60 rubles. (30 * 2). A worker has produced 50 parts.
- Calculation: 60 rub. * 50 parts = 3000 rub.;
2. Piece-progressive(worker output within the norm is paid at established rates; in excess of the norm, payment is made at increased piece rates).
Example: price per unit of production at a rate of 100 units is 40 rubles. Over 100 units the price increases by 10%. In fact, the worker produced 120 units.
- Calculation: 40 * 100 + (40 * 110% * 20) = 4880 rub.;
3. Piece-bonus(salary consists of earnings at basic rates and bonuses for fulfilling conditions and established bonus indicators).
Example: price per unit of production is 50 rubles. According to the provision on bonuses for the enterprise, in the absence of defects, a bonus is paid in the amount of 10% of earnings. In fact, the worker produced 80 units.
- Calculation: 50 * 80 + (4000 * 10%) = 4400 rubles;
4. Indirect piecework(earnings depend on the results of workers’ work).
Example: employee wages are set at 15% of the wages accrued to the team. The crew's earnings amounted to
15,000 rub.
- Calculation: 15000 * 15% = 2250 rub.;
5. Chord(the amount of payment is set for the entire range of work).
Time-based form of remuneration
Time-based is a form of remuneration in which wages to employees are calculated according to an established tariff schedule or salary for actual time worked.
For time-based wages Earnings for working hours are determined by multiplying the hourly or daily wage rate by the number of hours or days worked.
The time-bonus wage system has two forms:
1. Simple time-based(the hourly rate is multiplied by the number of hours worked).
Example: employee’s salary is 2000 rubles. In December, out of 22 working days, he worked 20 days.
- Calculation: 2000: 22 * 20 = 1818.18 rubles;
2. Time-bonus(a percentage increase is established on the monthly or quarterly salary).
Example: employee’s salary is 2000 rubles. Terms collective agreement a monthly bonus is provided in the amount of 25% of wages.
- Calculation: 2000 + (2000 * 25%) = 2500 rub.
Remuneration for managers, specialists and employees is made on the basis of official salaries established by the administration of the organization in accordance with the position and qualifications of the employee.
In addition to remuneration systems, remuneration for employees of organizations can be established based on the results of finished work. The amount of remuneration is determined taking into account the employee’s labor results and the length of his continuous work experience in the organization.
The administration of the enterprise may make additional payments in connection with deviations from normal working conditions in accordance with current legislation.
Night time is considered to be from 10 pm to 6 am. It is recorded on the timesheet every hour night work, is paid at an increased rate.
The following are not allowed to work at night: teenagers under 18 years of age, pregnant women, women with children under three years of age, disabled people.
Payment for work at night is made in the amount of 20% of the tariff rate of a time worker and piece worker, and in the case of multi-shift work - in the amount of 40%.
Overtime is considered work in excess of the established working day. Work overtime is documented in work orders or tables. Overtime work must not exceed four hours on two consecutive days or 120 hours per year.
Overtime work is paid for the first two hours at least one and a half times the rate, and for subsequent hours at least double the rate. Compensation overtime work Time off is not permitted.
On holidays, work is allowed, the suspension of which is impossible due to production and technical conditions.
If the day off coincides with holidays The day off is transferred to the next working day after the holiday. At the request of an employee working on a holiday, he may be given another day of rest.
Work on a holiday is paid at least twice as much:
- for piece workers - no less than double piece rates;
- employees whose work is paid at hourly or daily rates - at least double hourly or daily rate;
- for employees receiving a monthly salary - no less than a single hourly or daily rate in addition to their salary.
The amount of additional payments for combining professions in the same organization or performing the duties of a temporarily absent employee is established by the administration of the organization.
When performing work of various qualifications, the labor of temporary workers, as well as employees, is paid for work of a higher qualification. The labor of piece workers is based on the prices of the work performed.
When an employee is transferred to a lower-paid job, he retains his previous average earnings for two weeks from the date of transfer.
In cases where, as a result of the transfer of an employee, earnings decrease for reasons beyond his control, an additional payment is made to the previous average salary within two months from the date of transfer.
Downtime is documented in a downtime sheet, which indicates: downtime, reasons and culprits.
Downtime due to the fault of the employee is not paid, and not due to the fault of the employee - in the amount of 2/3 of the tariff rate established for the category of the employee.
Downtime can be used, i.e. workers during this time receive a new task or are assigned to another job. The work is documented by issuing work orders and the downtime sheet indicates the work order number and time worked.
There are marriages: correctable and irreparable, as well as marriages due to the fault of the employee and the fault of the organization.
Defects not caused by the employee are paid in the amount of 2/3 of the tariff rate of a temporary worker of the corresponding category for the time that should be spent on this work according to the norm.
Marriage is formalized by deed. If the worker made a mistake and corrected it himself, then the act is not drawn up. When the defect is corrected, other workers are issued an order for piecework work with a note about the correction of the defect.
Wages for unworked hours
Payment for unworked time includes: payment for annual leave, main and additional, payment for educational leave, payment of compensation for leave upon dismissal, payment of severance pay upon dismissal, payment for downtime not due to the employee’s fault, payment for forced absence, payment for preferential hours for nursing mothers .
Procedure for granting and paying annual and additional leave
Annual paid leave is provided to employees of at least 24 working days per six-day working week or at least 28 calendar days. In the first year of an employee’s work at the enterprise, he can be granted leave no earlier than 6 months after the start of work.
Temporary and seasonal workers have the right to paid leave on a general basis. But if temporary workers employment contract worked up to 4 months, and seasonal workers - up to 6 months, then they are not entitled to vacation. Home workers are granted leave on a general basis.
Employees who took absenteeism without good reason, paid leave is reduced by the number of days of absenteeism.
Some categories of employees enjoy the right to extended leave. These categories include: younger workers
18 years old, employees educational institutions, children's institutions, research institutions, other categories of workers, the duration of vacation of which is established in accordance with legislative acts.
Additional annual leave provided to: workers with irregular working hours, workers of the Far North and equivalent areas, workers engaged in work with harmful conditions labor.
If an employee falls ill while on regular leave, the leave is extended for the days of illness.
If an employee falls ill while on additional leave, the leave is not extended and is not transferred to another period.
When maternity leave comes due during the next leave, the latter is interrupted and granted at any other time at the request of the employee.
If an employee quits before the end of the working year for which he has already received vacation, then the amount for unworked vacation days is withheld from him.
Deductions for days of incapacity for work are not made in the following cases: if upon dismissal the employee is not due payments, the employee is called up for military service, reduction of the organization's staff, as well as in the event of liquidation, retirement, assignment to study, absence from work for more than four months in a row due to temporary disability, or the employee's inadequacy for the position held.
Example: calculation for the next vacation, when all months of the billing period have been fully worked.
The employee goes on vacation in May. Vacation payments are made based on the three previous months: February, March, April.
- Monthly salary - 1800 rubles.
- The average number of days in a month is 29.6.
- Average daily earnings are:
- (1800 + 1800 + 1800) : 3: 29.6 = 60.8 rub.
- The amount of vacation pay will be:
- 60.8 * 28 = 1702.4 rubles.
The actual accrued amounts of regular and additional vacations, compensation for used vacations are included in production and distribution costs.
Organizations can create a reserve to accrue vacations, which is taken into account in account 96 “Reserve for future expenses.” When forming a reserve, a posting is made: debit to account 20 “Main production” and credit to account 96 “Reserve for future expenses”. When employees actually go on vacation: debit account 96 and credit account 70 “Calculations for wages”. The percentage of contributions to the reserve is determined as the ratio of the amount required to pay for vacations in the coming year to the total wage fund for the coming year.
Example: annual payroll of the organization - 90,000,000 rubles, amount for vacation pay - 6,300,000 rubles, percentage of monthly contributions to the vacation reserve - 6,300,000: 90,000,000 * 100% = 7%.
Monthly contributions to the wage reserve are calculated using the formula: 3P + Social Insurance Fund + Pension Fund + Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund: 100% * Pr,
- where ZP is the actual salary accrued for the reporting period;
- FSS - contributions to the Fund social insurance RF;
- PF - contributions to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation;
- MHIF - contributions to the Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation;
- Pr - percentage of monthly deductions.
Calculation of temporary disability benefits
The basis for payment of benefits is a certificate of incapacity for work issued by a medical institution. Temporary disability benefits are issued from the first day of payment of the ability to work. In case of a domestic injury, benefits are issued from the sixth day of incapacity for work. If the injuries were the result of a natural disaster, benefits are issued for the entire period of incapacity.
Benefit for temporary disability due to work injury and occupational disease is paid in the amount of full earnings, and in other cases - depending on the duration of continuous work experience, including minor dependent children. So, for less than 5 years of experience - 45% of the actual salary, from 5 to 8 years - 65% and over 8 years - 85%.
The amount of temporary disability benefits paid is calculated on the basis of average earnings. To calculate average earnings, you need to add up the amounts that were accrued to the employee over the previous 12 months and divide the result by the number of days worked during this period. This procedure is established by Article 139 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
If during the billing period the employee did not receive a salary or did not work at all, then the average earnings are calculated based on payments for the previous period equal to the billing period. If an employee has not yet worked at the enterprise for 12 months, only those months in which he has already worked should be taken into account.
Women's allowance registered in medical institutions in the early stages of pregnancy.
To pay benefits, women are issued a certificate from the antenatal clinic confirming registration. The benefit is paid simultaneously with maternity benefits. When an organization is liquidated, a one-time benefit is paid from the funds of the Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation in the amount of the monthly minimum wage. Payment of benefits is made from social insurance funds.

 Surely, every employee would like his wages to meet his needs, wages that would allow him to provide his family with everything necessary. When setting wages, the employer takes into account production costs, the prevailing level of wages in the industry, and also expects to make a profit.
Surely, every employee would like his wages to meet his needs, wages that would allow him to provide his family with everything necessary. When setting wages, the employer takes into account production costs, the prevailing level of wages in the industry, and also expects to make a profit.